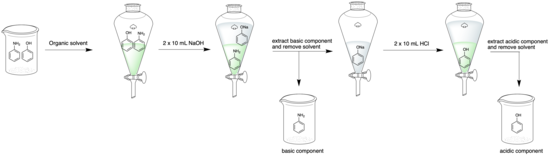
Acid–base extraction
[1] It is typically performed during the work-up step following a chemical synthesis to purify crude compounds[2] and results in the product being largely free of acidic or basic impurities.
[3] Acid-base extraction utilizes the difference in solubility of a compound in its acid or base form to induce separation.
[4] Typically, the desired compound is changed into its charged acid or base form, causing it to become soluble in aqueous solution and thus be extracted from the non-aqueous (organic) layer.
[3][7] The following procedure is typically followed when performing an acid-base extraction for a mixture containing an acidic and/or basic compound: Acid-base extraction is frequently used as the first step in a work-up procedure following a chemical synthesis[2] to remove acidic and basic starting materials or impurities.
[3] Acid-base extraction is typically a precursor to more complicated purification techniques, such as recrystallization, if the product synthesized is still not completely pure.
The post-reaction mixture often consists of small amounts of leftover acid and alcohol, in addition to the desired ester.
Another common example of acid-base extraction occurs following peptide coupling, where the amide product must be separated from leftover carboxylic acid and amine.