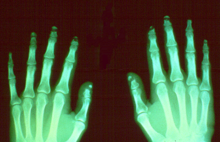
Acroosteolysis
Acroosteolysis is resorption of the distal bony phalanges.
Acroosteolysis has two patterns of resorption in adults: diffuse and bandlike.
The diffuse pattern of resorption has a widely diverse differential diagnosis which includes: pyknodysostosis, collagen vascular disease and vasculitis, Raynaud's neuropathy, trauma, epidermolysis bullosa, psoriasis, frostbite, sarcoidosis, hypertrophic osteoarthropathy, acromegaly, and advanced leprosy.
[1][2][3] The bandlike pattern of resorption may be seen with polyvinyl chloride exposure and Hadju-Cheney syndrome.
[4] Pyknodysostosis, Psoriasis, Injury (thermal burn, frostbite), Neuropathy (diabetes), Collagen vascular disease (scleroderma, Raynaud's), Hyperparathyroidism, Familial (Hadju-Cheney, progeria), Occupational (polyvinyl exposure), Acroosteolysis may be associated with minimal skin changes or with ischemic skin lesions that may result in digital necrosis.