Advanced airway management
It encompasses various techniques performed to create an open or patent airway – a clear path between a patient's lungs and the outside world.
Common methods of assessing difficult airways include a Mallampati score, Cormack-Lehane classification, thyromental distance, degree of mouth opening, neck range of motion, body habitus, and malocclusion (underbite or overbite).
A recent Cochrane systematic review examines the sensitivity and specificity of the various bedside tests commonly used to predict difficulty in airway management.
[3][4] An oropharyngeal airway (OPA) is a rigid tube that is inserted into the mouth through the oropharynx and placed above the tongue to move it away from the back of the throat.
[2][4][3] Complications from OPA placement include damage to the teeth and the lingual nerve, which may cause changes in taste and sensation of the tongue.
[5][4] Each type of EGD has different features, including the ability to remove air from the stomach (gastric decompression) and perform tracheal intubation.
[3][5] Supraglottic airway devices (SGAs) create a seal over the glottic opening to route oxygen directly into the trachea.
[3][5][4] Success rates of SGAs in securing airways are similar between the different models, and these devices provide effective ventilation in more than 98% of patients.
[4] Retroglottic airway devices (RGAs) pass behind the glottis and into the esophagus to create a seal allowing oxygen to be delivered directly to the trachea.
[4] Tracheal intubation, often simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic or rubber endotracheal tube (ETT) into the trachea to maintain an open airway, allow for effective ventilation, protect the airway from aspiration (when a cuffed ETT is used), and to serve as a conduit through which to administer inhaled anesthetics.
There are multiple different laryngoscope blade styles, shapes, and lengths from which to choose based on patient anatomy and clinician preference.
Regardless of blade shape, direct laryngoscopy technique involves passage of the laryngoscope through the mouth and into the back of the throat.
Manipulation of the neck and lifting of the tongue allows for direct visualization of the larynx and vocal cords by the operator.
[9] The GlideScope model utilizes a curved laryngoscopic blade with an integrated camera connected to a large external monitor.
The fiberoptic scope is flexible and can be directed by the operator, allowing it to traverse the upper airway with minimal manipulation of the patient's neck.
Some of the more popular techniques include Lightwand intubation that uses an LED lit stylet to transilluminate the soft tissues of the neck if correctly placed in the trachea and then inserting an endotracheal tube through it.
Surgical airway management is performed as a last resort in cases where tracheal intubation has failed, is not feasible, or is contraindicated.
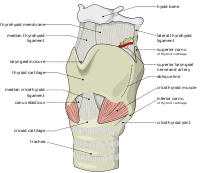
[19][20] A cricothyrotomy is a procedure during which an incision is made through the cricothyroid membrane, allowing an artificial airway to be placed in the trachea.
It is the first-line surgical procedure to access an airway in an emergency because it can be performed more quickly than a tracheotomy and is less likely to cause bleeding and damage to thyroid tissue.
[20] A cricothyrotomy is typically performed as an emergency procedure when other airway management attempts have failed and the patient is at risk of asphyxiation.
[24] The most common acute complications of a tracheotomy are difficulty speaking or swallowing due to nerve damage, prolonged bleeding at the incision site, and pneumothorax.
The algorithm provides a step-by-step framework to respond to situations where traditional airway management techniques may be inadequate.
[27] Children have numerous anatomic differences from adults which present unique challenges when implementing advanced airway techniques.
Broselow tape is a tool used to help facilitate rapid and accurate equipment sizing decisions in pediatric emergency situations.
Surgical help should be requested for invasive access, however, in scenarios in which a pediatric otorhinolaryngologist is not available, a needle cricothyrotomy is an emergency alternative.