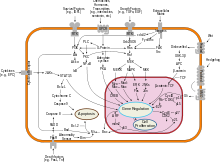
Cytokine
Cytokines (/ˈsaɪtəkaɪn/)[1] are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa[2]) important in cell signaling.
Cytokines are important in health and disease, specifically in host immune responses to infection, inflammation, trauma, sepsis, cancer, and reproduction.
[5] The activity of interferon-gamma (the sole member of the interferon type II class) was described in 1965; this was the first identified lymphocyte-derived mediator.
[6] Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) was identified simultaneously in 1966 by John David and Barry Bloom.
(not to be confused with the Nobel laureate named Stanley Cohen, who was a PhD biochemist; nor with the MD geneticist Stanley Norman Cohen) published an article describing the production of MIF in virus-infected allantoic membrane and kidney cells, showing its production is not limited to immune cells.
[11] Classic hormones circulate in aqueous solution in nanomolar (10-9 M) concentrations that usually vary by less than one order of magnitude.
For instance, to accurately utilize hormone terminology, cytokines may be autocrine or paracrine in nature, and chemotaxis, chemokinesis and endocrine as a pyrogen.
Cytokines have been classed as lymphokines, interleukins, and chemokines, based on their presumed cell of secretion, function, or target of action.
Structural homogeneity has been able to partially distinguish between cytokines that do not demonstrate a considerable degree of redundancy so that they can be classified into four types: A classification that proves more useful in clinical and experimental practice outside of structural biology divides immunological cytokines into those that enhance cellular immune responses, type 1 (TNFα, IFN-γ, etc.
Cytokines also play a role in anti-inflammatory pathways and are a possible therapeutic treatment for pathological pain from inflammation or peripheral nerve injury.
This may include the upregulation and/or downregulation of several genes and their transcription factors, resulting in the production of other cytokines, an increase in the number of surface receptors for other molecules, or the suppression of their own effect by feedback inhibition.
[32] A 2024 study found a positive correlation between plasma interleukin IL-2 and fatigue in patients with type 1 narcolepsy.
Forkhead box protein 3 (Foxp3) as a transcription factor is an essential molecular marker of Treg cells.
Cytokines are integral and implicated in all angles of the cascade, resulting in the systemic inflammatory response syndrome and multi-organ failure associated with this intra-abdominal catastrophe.
[41][42][43] Current data suggest cytokine storms may be the source of extensive lung tissue damage and dysfunctional coagulation in COVID-19 infections.