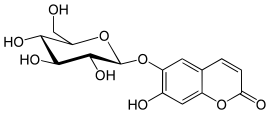
Aesculin
Aesculin, also called æsculin or esculin, is a coumarin glucoside that naturally occurs in the trees horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum),[1] California buckeye (Aesculus californica),[2] prickly box (Bursaria spinosa), and daphnin (the dark green resin of Daphne mezereum).
[3] Aesculin is also used in a microbiology laboratory to aid in the identification of bacterial species (especially Enterococci and Listeria[4]).
In fact, all strains of Group D Streptococci hydrolyze æsculin in 40% bile.
Aesculetin forms dark brown or black complexes with ferric citrate, allowing the test to be read.
The presence of a dark brown or black halo indicates that the test is positive.