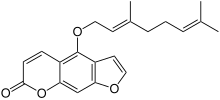
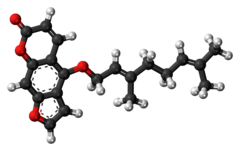
Bergamottin
Bergamottin and dihydroxybergamottin are linear furanocoumarins functionalized with side chains derived from geraniol.
Drugs that may have limited use because they are metabolized by CYP3A4 may become viable medications when taken with a CYP3A4 inhibitor because the dose required to achieve a necessary concentration in the blood would be lowered.
[4] An example of the use of this effect in current medicines is the co-administration of ritonavir, a potent inhibitor of the CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 isoforms of cytochrome P450, with other antiretroviral drugs.
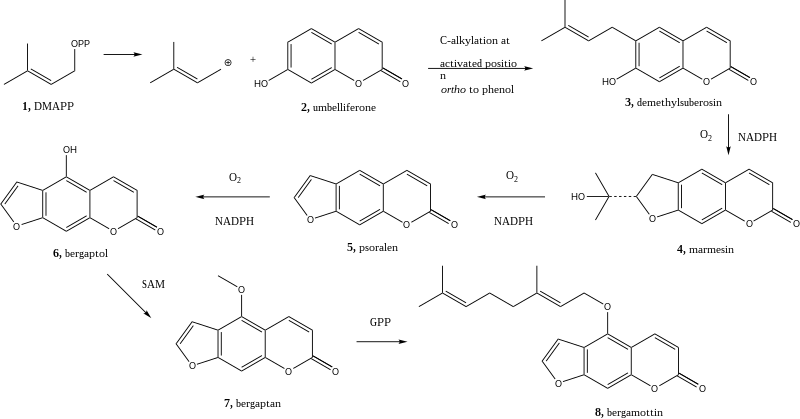
The cyclization of an alkyl group occurs to form marmesin (4), which is done in the presence of NADPH and oxygen along with a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase catalyst.
The final step in this biosynthesis is the attachment of a GPP, or geranyl pyrophosphate, to the newly methylated bergapten (7) to form the target molecule bergamottin (8).