Amyloplast
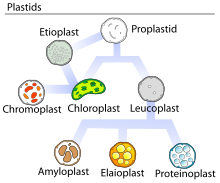
Amyloplasts are a type of plastid, double-enveloped organelles in plant cells that are involved in various biological pathways.
[1][2] Amyloplasts are found in roots and storage tissues, and they store and synthesize starch for the plant through the polymerization of glucose.
[2][3] Starch synthesis and storage also takes place in chloroplasts, a type of pigmented plastid involved in photosynthesis.
Statoliths, a specialized starch-accumulating amyloplast, are denser than cytoplasm, and are able to settle to the bottom of the gravity-sensing cell, called a statocyte.
[8] This mutant shows a significantly weaker gravitropic response as compared to a non-mutant plant.