Anatomical terms of bone
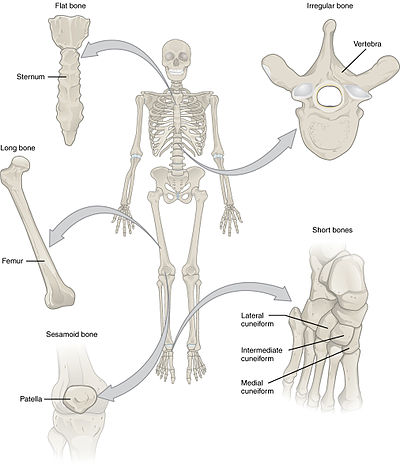
[1] A short bone is one that is cube-like in shape, being approximately equal in length, width, and thickness.
Examples include the cranial (skull) bones, the scapulae (shoulder blades), the sternum (breastbone), and the ribs.
Flat bones serve as points of attachment for muscles and often protect internal organs.
These bones tend to have more complex shapes, like the vertebrae that support the spinal cord and protect it from compressive forces.
The sesamoid bones protect tendons by helping them overcome compressive forces.
These terms are derived from tuber (Latin: swelling).,[8] as is also protuberance, which occasionally is synonymous with "tuberosity".
[citation needed] A line refers to a long, thin projection, often with a rough surface.
[11] [b] A spine, as well as referring to the spinal cord, may be used to describe a relatively long, thin projection or bump.
The medial malleolus is the prominence on the inner side of the ankle, formed by the lower end of the tibia.
The lateral malleolus is the prominence on the outer side of the ankle, formed by the lower end of the fibula.
A canal is a long, tunnel-like foramen, usually a passage for notable nerves or blood vessels.
[citation needed] This Wikipedia entry incorporates text from the freely licensed Connexions [1] edition of Anatomy & Physiology [2] text-book by OpenStax College