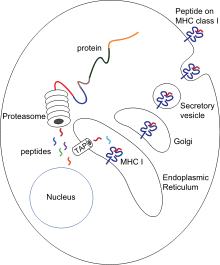
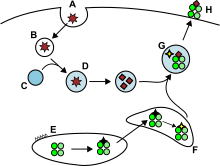
Antigen presentation
Specifically, the fragment, bound to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), is transported to the surface of the antigen-presenting cell, a process known as presentation.
If there has been an infection with viruses or bacteria, the antigen-presenting cell will present an endogenous or exogenous peptide fragment derived from the antigen by MHC molecules.
This antigen presentation pathway enables the immune system to detect transformed or infected cells displaying peptides from modified-self (mutated) or foreign proteins.
[5][6] In the presentation process, these proteins are mainly degraded into small peptides by cytosolic proteases in the proteasome, but there are also other cytoplasmic proteolytic pathways.
[citation needed] APCs usually internalise exogenous antigens by endocytosis, but also by pinocytosis, macroautophagy, endosomal microautophagy or chaperone-mediated autophagy.
Peptide-MHC-II complexes (pMHC-II) are transported to the plasma membrane and the processed antigen is presented to the helper T cells in the lymph nodes.
[9] APCs undergo a process of maturation while migrating, via chemotactic signals, to lymphoid tissues, in which they lose the phagocytic capacity and develop an increased ability to communicate with T-cells by antigen-presentation.
[citation needed] B-cell receptors on the surface of B cells bind to intact native and undigested antigens of a structural nature, rather than to a linear sequence of a peptide which has been digested into small fragments and presented by MHC molecules.
Some APCs expressing comparatively lower levels of lysosomal enzymes are thus less likely to digest the antigen they have captured before presenting it to B cells.