Arabs
[76] Throughout the Ancient Near East, Arabs established influential civilizations starting from 3000 BCE onwards, such as Dilmun, Gerrha, and Magan, playing a vital role in trade between Mesopotamia, and the Mediterranean.
[87] During late antiquity, the Tanukhids, Salihids, Lakhmids, Kinda, and Ghassanids were dominant Arab tribes in the Levant, Mesopotamia, and Arabia, they predominantly embraced Christianity.
[93] Arabs have significantly influenced and contributed to human progress in many fields, including science, technology, philosophy, ethics, literature, politics, business, art, music, comedy, theatre, cinema, architecture, food, medicine, and religion.
[96] The earliest documented use of the word Arab in reference to a people appears in the Kurkh Monoliths, an Akkadian-language record of the Assyrian conquest of Aram (9th century BCE).
Other Ancient-Greek historians like Agatharchides, Diodorus Siculus and Strabo mention Arabs living in Mesopotamia (along the Euphrates), in Egypt (the Sinai and the Red Sea), southern Jordan (the Nabataeans), the Syrian steppe and in eastern Arabia (the people of Gerrha).
[121] The Quran mentions that Ibrahim (Abraham) and his wife Hajar (Hagar) bore a prophetic child named Ishmael, who was gifted by God a favor above other nations.
"[125] The Targum Onkelos annotates (Genesis 25:16), describing the extent of their settlements: The Ishmaelites lived from Hindekaia (India) to Chalutsa (possibly in Arabia), by the side of Mizraim (Egypt), and from the area around Arthur (Assyria) up towards the north.
Magan (Arabic: مِجَانُ, Majan), known for its production of copper and other metals, the region was an important trading center in ancient times and is mentioned in the Qur'an as a place where Musa (Moses) traveled during his lifetime.
[149] Limited local historical coverage of these civilizations means that archaeological evidence, foreign accounts and Arab oral traditions are largely relied on to reconstruct this period.
These highly valued aromatic resins were exported to Egypt, Greece, and Rome, making the Sabaeans wealthy and powerful, they also traded in spices, textiles, and other luxury goods.
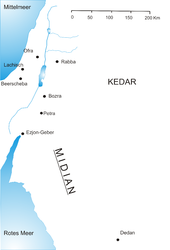
[165][166][160] Lihyan also called Dadān or Dedan was a powerful and highly organized ancient Arab kingdom that played a vital cultural and economic role in the north-western region of the Arabian Peninsula and used Dadanitic language.
[203] The Kingdom of Hatra was an ancient city located in the region of Mesopotamia, it was founded in the 2nd or 3rd century BCE and flourished as a major center of trade and culture during the Parthian Empire.
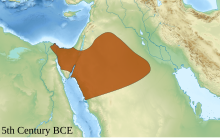
They returned to Yemen and allied themselves with the Himyarites who installed them as a vassal kingdom that ruled Central Arabia from "Qaryah Dhat Kahl" (the present-day called Qaryat al-Faw).
Overall, the Rashidun era played a crucial role in shaping Arab history and continues to be revered by Muslims worldwide as a period of exemplary leadership and guidance.
[224] Caliph Umar II strove to resolve the conflict when he came to power in 717, demanding that all Muslims be treated as equals, but his intended reforms did not take effect, as he died after only three years of rule.
During this period the Arab Empire became an intellectual centre for science, philosophy, medicine and education as the Abbasids championed the cause of knowledge and established the "House of Wisdom" in Baghdad.
[226] The Abbasids ruled for 200 years before they lost their central control when Wilayas began to fracture in the 10th century; afterwards, in the 1190s, there was a revival of their power, which was ended by the Mongols, who conquered Baghdad in 1258 and killed the Caliph Al-Musta'sim.
The empire was based in North Africa, with its capital in Cairo, and at its height, it controlled a vast territory that included parts of modern-day Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco, Syria, and Palestine.
Similar attempts were made by other Arab leaders, such as Hafez al-Assad, Ahmed Hassan al-Bakr, Faisal I of Iraq, Muammar Gaddafi, Saddam Hussein, Gaafar Nimeiry and Anwar Sadat.
[256] The United Arab Republic (UAR) was a political union formed between Egypt and Syria in 1958, with the goal of creating a federal structure that would allow each member state to retain its identity and institutions.
[403][404] The most popular beasts and demons of Arabian mythology are Bahamut, Dandan, Falak, Ghoul, Hinn, Jinn, Karkadann, Marid, Nasnas, Qareen, Roc, Shadhavar, Werehyena and other assorted creatures which represented the profoundly polytheistic environment of pre-Islamic.
Al-Jāḥiẓ was also one of the first Arabian writers to suggest a complete overhaul of the language's grammatical system, though this would not be undertaken until his fellow linguist Ibn Maḍāʾ took up the matter two hundred years later.
It is characterized by a variety of herbs and spices, including cumin, coriander, cinnamon, sumac, za'atar, cardamom, mint, saffron, sesame, thyme turmeric and parsley.
Beginning in the mid-1980s, Lydia Canaan, musical pioneer widely regarded as the first rock star of the Middle East[472][473] Arab polytheism was the dominant religion in pre-Islamic Arabia.
[480] Nomadic religious belief systems and practices are believed to have included fetishism, totemism and veneration of the dead but were connected principally with immediate concerns and problems and did not consider larger philosophical questions such as the afterlife.
[481] Most notable Arab gods and goddesses: 'Amm, A'ra, Abgal, Allah, Al-Lat, Al-Qaum, Almaqah, Anbay, ʿAṯtar, Basamum, Dhu l-Khalasa, Dushara, Haukim, Hubal, Isāf and Nā'ila, Manaf, Manāt, Nasr, Nuha, Quzah, Ruda, Sa'd, Shams, Samas, Syn, Suwa', Ta'lab, Theandrios, al-'Uzzá, Wadd, Ya'uq, Yaghūth, Yatha, Aglibol, Astarte, Atargatis, Baalshamin, Bēl, Bes, Ēl, Ilāh, Inanna/Ishtar, Malakbel, Nabū, Nebo, Nergal, Yarhibol.
The first great Arab thinker in the Islamic tradition is widely regarded to be al-Kindi (801–873 A.D.), a Neo-Platonic philosopher, mathematician and scientist who lived in Kufa and Baghdad (modern day Iraq).
After being appointed by the Abbasid Caliphs to translate Greek scientific and philosophical texts into Arabic, he wrote a number of original treatises of his own on a range of subjects, from metaphysics and ethics to mathematics and pharmacology.
[483][484] Arabic science underwent considerable development during the Middle Ages (8th to 13th centuries CE), a source of knowledge that later spread throughout Medieval Europe and greatly influenced both medical practice and education.
[488] The pious scholars of Islam, men and women collectively known as the ulama, were the most influential element of society in the fields of Sharia law, speculative thought and theology.