Upper Mesopotamia
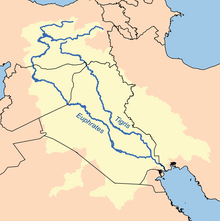
Upper Mesopotamia constitutes the uplands and great outwash plain of northwestern Iraq, northeastern Syria and southeastern Turkey, in the northern Middle East.
[2] The Euphrates and Tigris rivers transform Mesopotamia into almost an island, as they are joined together at the Shatt al-Arab in the Basra Governorate of Iraq, and their sources in eastern Turkey are in close proximity.
[citation needed] In pre-Abbasid times the western and eastern boundaries seem to have fluctuated, sometimes including what is now northern Syria to the west and Adiabene in the east.
[citation needed] Al-Jazira is characterised as an outwash or alluvial plain, quite distinct from the Syrian Desert and lower-lying central Mesopotamia; however, the area includes eroded hills and incised streams.
This is the area where the earliest signs of agriculture and domestication of animals have been found, and thus the starting point leading to civilization and the modern world.
Al-Jazirah includes the mountain Karaca Dağ in southern Turkey, where the closest relative to modern wheat still grows wild.
From Al-Jazirah the idea of farming along with the domesticated seeds spread first to the rest of the Levant and then to North-Africa, Europe and eastwards through Mesopotamia all the way to present-day Pakistan (see Mehrgarh).
This raises questions about whether (semi)sedentary hunter-gatherer communities were sufficiently affluent and numerous to coordinate and carry out large-scale communal construction projects.
Since pre-Arab and pre-Islamic times, al-Jazira has been an economically prosperous region with various agricultural (fruit and cereal) products, as well as a prolific manufacturing (food processing and cloth weaving) system.
During the early Umayyad Caliphate, the administration of al-Jazira was often shared with that of Arminiya, a vast province encompassing most of Transcaucasia, Eastern Anatolia and what is now Iranian Azerbaijan.
The prosperity of the region and its high agricultural and manufacturing output made it an object of contest between the leaders of the early conquering Arab armies.
At the turn of the 11th century, the area came under the rule of a number of local dynasties, the Numayrids, the Mirdasids, and the Uqaylids, who persisted until the conquest by the Seljuq Empire.
Thereafter the northern and eastern portions were ruled initially by the Artuqids, laterly by the Kara Koyunlu and Akkoyunlu Turcomans and finally by the Safavids; while the western parts came under the Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt until the Ottoman–Mamluk War (1516–17), when it was taken by the Ottoman Empire.
Although the region is ethnically diverse, it is considered to be the traditional Assyrian homeland in addition to Aramaic-speaking Christian descendants of the ancient Mesopotamians.
[14] In the middle of the 19th century, and due to the wars between the Kurdish Buhti amirs and the Turks, many Christians in the Siirt area were killed by the Kurds.
After the failed Kurdish rebellions in Kemalist Turkey in the mid 1920s, there was a large influx of Kurds to Syrian Jazira province, that fell under the occupation of French Mandate authorities to escape the subsequent Turkish onslaught.
It is estimated that 25,000 Kurds fled at this time to northern Syria, under French Mandate authorities, who encouraged their immigration,[16] and granted them Syrian citizenship.
Even though the assault failed, the Assyrians were terrorized and left in large numbers, and the immigration of Kurds from Turkey to the area have converted al-Malikiya, al-Darbasiyah and Amuda to completely Kurdish cities.