Arthrogryposis
Types of arthrogryposis with a primary neurological or muscle disease belong to the syndromic group.
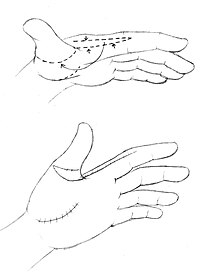
[4] Every joint in the body, when affected, displays typical signs and symptoms: for example, the shoulder (internal rotation); wrist (volar and ulnar); hand (fingers in fixed flexion and thumb in palm); hip (flexed, abducted and externally rotated, frequently dislocated); elbow (extension and pronation) and foot clubfoot and less commonly congenital vertical talus.
There are a few slightly more common diagnoses such as pulmonary hypoplasia, cryptorchidism, congenital heart defects, tracheoesophageal fistulas, inguinal hernias, cleft palate, and eye abnormalities.
[2] Seventy to eighty percent of cases of the most severe forms of arthrogryposis are caused by neurological abnormalities, which can be either genetic or environmental.
[10] It could be found during routine ultrasound scanning showing a lack of mobility and abnormal position of the foetus.
[2] In clinic a child can be diagnosed with arthrogryposis with physical examination, confirmed by ultrasound, MRI,[3][10] or muscle biopsy.
Another vital intervention that occupational therapists use to treat arthrogryposis, is range of motion exercises.
[44] The primary long-term goals of these treatments are increasing joint mobility and muscle strength and the development of adaptive use patterns that allow for walking and independence with activities of daily living.
For example, the Wilmington Robotic Exoskeleton is a potential assistive device built on a back brace, shadowing the upper arm and forearm.
[45][46][47] Researchers at the University of Delaware are developing a light and unobtrusive therapeutic garment, suitable for babies and children, called the Playskin Lift.
[2] Dorsal carpal wedge osteotomy is indicated for wrists with excessive flexion contracture deformity when non-surgical interventions such as occupational therapy and splinting have failed to improve function.
This tissue can be used to resurface the thumb-index web after a comprehensive release of all the tight structures to allow for a larger range of motion of the thumb.
The flap is made as wide as possible, but still small enough to close with the excessive skin on the palmar side of the index finger.
In the early years of life the serial casting according to the Ponseti method usually yields good results.
It is usually accompanied by soft tissue surgery in the form of release of contracted tendon and capsular structures.
[54] Less frequent patients with arthrogryposis may develop congenital vertical talus also known as rocker bottom foot.
Similarly, congenital vertical talus is classically managed by serial casting according to the reversed Ponseti method.
Naviculectomy or midtarsal resection arthroplasty represents a less invasive option with satisfactory short-term results.
There is no way to resolve or cure AMC completely but with proper treatment most children make significant improvements in their range of motion and ability to move their limbs, which enables them to carry out daily activities and live relatively normal lives.
[citation needed] Therapeutic interventions that are cornerstones in the treatment of AMC include: stretching and range of motion exercises, physical, occupational and speech therapy, splinting and serial casting.