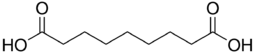
Azelaic acid
It is a precursor to diverse industrial products including polymers and plasticizers, as well as being a component of several hair and skin conditioners.
[7] It serves as a signal that induces the accumulation of salicylic acid, an important component of a plant's defensive response.
[8] The mechanism of action in humans is thought to be through the inhibition of hyperactive protease activity that converts cathelicidin into the antimicrobial skin peptide LL-37.
It also decreases the production of keratin, which is a natural substance that promotes the growth[clarification needed] of acne bacteria.
[26] According to one report in 1988, azelaic acid in combination with zinc sulfate in vitro was found to be a potent (90% inhibition) 5α-reductase inhibitor, similar to the hair loss drugs finasteride and dutasteride.
[27] In vitro research during mid-1980s evaluating azelaic acid's depigmenting (whitening) capability concluded it is effective (cytotoxic to melanocytes) at only high concentrations.