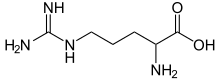
Arginine
At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) and both the amino and guanidino groups are protonated, resulting in a cation.
[5][6] He named it from the Greek árgyros (ἄργυρος) meaning "silver" due to the silver-white appearance of arginine nitrate crystals.
[13] Arginine is classified as a semiessential or conditionally essential amino acid, depending on the developmental stage and health status of the individual.
[14] Preterm infants are unable to synthesize arginine internally, making the amino acid nutritionally essential for them.
[15] Most healthy people do not need to supplement with arginine because it is a component of all protein-containing foods[16] and can be synthesized in the body from glutamine via citrulline.
[17][18] Additional, dietary arginine is necessary for otherwise healthy individuals temporarily under physiological stress, for example during recovery from burns, injury or sepsis,[18] or if either of the major sites of arginine biosynthesis, the small intestine and kidneys, have reduced function, because the small bowel does the first step of the synthesizing process and the kidneys do the second.
[19] For some carnivores, for example cats, dogs[20] and ferrets, arginine is essential,[3] because after a meal, their highly efficient protein catabolism produces large quantities of ammonia which need to be processed through the urea cycle, and if not enough arginine is present, the resulting ammonia toxicity can be lethal.
This is demonstrated by the fact that, in many cell types, nitric oxide synthesis can be supported to some extent by citrulline, and not just by arginine.
[24] Arginine plays an important role in cell division, wound healing, removing ammonia from the body, immune function,[25] and the release of hormones.
[38] The amino acid side-chain of arginine consists of a 3-carbon aliphatic straight chain, the distal end of which is capped by a guanidinium group, which has a pKa of 13.8,[39] and is therefore always protonated and positively charged at physiological pH.
[45] A 2017 study concludes that "clinicians could consider advising patients that there is a theoretical role of lysine supplementation in the prevention of herpes simplex sores but the research evidence is insufficient to back this.
Assays also confirmed significantly reduced levels of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), but increased agmatine concentration and glutamate/GABA ratio in the schizophrenia cases.
Regression analysis indicated positive correlations between arginase activity and the age of disease onset and between L-ornithine level and the duration of illness.
Despite this, the biological basis of schizophrenia is still poorly understood, a number of factors, such as dopamine hyperfunction, glutamatergic hypofunction, GABAergic deficits, cholinergic system dysfunction, stress vulnerability and neurodevelopmental disruption, have been linked to the aetiology and/or pathophysiology of the disease.