Beach nourishment
Nourishment is typically a repetitive process because it does not remove the physical forces that cause erosion; it simply mitigates their effects.
Since then more shoreface nourishments have been carried out, which rely on the forces of the wind, waves and tides to further distribute the sand along the shore and onto the beaches and dunes.
There are numerous incidences of the modern recession of beaches, mainly due to a gradient in longshore drift and coastal development hazards.
During calm weather, smaller waves return sand from bars to the visible beach surface in a process called accretion.
Continuous, long-term renourishment efforts, especially in cuspate-cape coastlines, can play a role in longshore transport inhibition and downdrift erosion.
A wide beach is a good energy absorber, which is significant in low-lying areas where severe storms can impact upland structures.
The effectiveness of wide beaches in reducing structural damage has been proven by field studies conducted after storms and through the application of accepted coastal engineering principles.
Imported sand may differ in character (chemical makeup, grain size, non-native species) from that of the target environment.
Related attempts to reduce future erosion may provide a false sense of security that increases development pressure.
[25] The selection of suitable material for a particular project depends upon the design needs, environmental factors and transport costs, considering both short and long-term implications.
Excess silt and clay fraction (mud) versus the natural turbidity in the nourishment area disqualifies some materials.
Evaluating material fit requires a sand survey that usually includes geophysical profiles and surface and core samples.
The Gold Coast profile nourishment program placed 75% of its total sand volume below low water level.
[28] Techniques for incorporating nourishment projects into flood insurance costs and disaster assistance remain controversial.
[29] The performance of a beach nourishment project is most predictable for a long, straight shoreline without the complications of inlets or engineered structures.
[citation needed] Nourishment can affect eligibility in the U.S. National Flood Insurance Program and federal disaster assistance.
The groundwater enters the PEM tube allowing gravity to conduct it to a coarser sand layer, where it can drain more quickly.
[citation needed] Another approach is to create dynamic revetment, a berm using unmortared, unsorted rocks (cobbles).
Restoration in Cancun was expected to deliver 1.3 billion US gallons (4,900,000 m3) of sand to replenish 450 meters (1,480 ft) of coastline.
In the Coastal Memorandum of 1990 the government decided, after a very detailed study, that all erosion along the full Dutch coastline would be compensated by artificial beach nourishment.
[44] The shoreline is closely monitored by yearly recording of the cross section at points 250 meters (820 ft) apart, to ensure adequate protection.
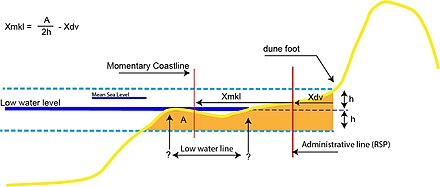
Each year, the shoreline to be tested ( TKL) is determined on the basis of the MKL, and if it threatens to come inland from the BKL, a sand nourishment is carried out.
The recipe for calculating the position of the MKL is:[48] The background of this method is that the thickness of the sand layer to be taken must be a function of the measuring wave height; however, it is unknown.
From the period from about 1850 there are also profile soundings available in some places, but these are often slightly shifted compared to the jarkus rowing and are therefore more difficult to analyse.
A nourishment design for coastal maintenance and beach widening can be made much more reliable based on measurement data, provided that they are present.
This is in fact moving the tidal channel further from the coastline [56](chapter 4) Instead of directly supplying the beach, it is also possible to supple the foreshore (underwater bank).
[60] A second project, along Stable Road, that attempted to slow rather than halt erosion, was stopped halfway toward its goal of adding 10,000 cubic yards (7,600 m3) of sand.
[60] Supporters claimed that 2010's seasonal summer erosion was less than in prior years, although the beach was narrower after the restoration ended than in 2008.
[citation needed] Florida - Ninety PEMs (Pressure Equalizing Modules) were installed in February 2008 at Hillsboro Beach.
[70] Justifications for the projects, controversial within New Jersey, have included flood control, prevention of damage to waterfront residences, and protection of summer tourism along the shore,[69] as well as public access to beaches.