Biogerontology
[2] James Vaupel has predicted that life expectancy in industrialized countries will reach 100 for children born after the year 2000.
A relatively new interdisciplinary field called geroscience focuses on preventing diseases of aging and prolonging the 'healthspan' over which an individual lives without serious illness.
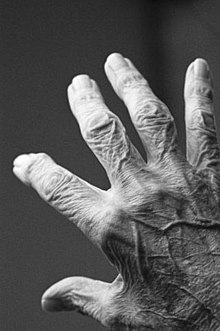
Cells and tissues are injured due to the accumulation of damage over time resulting in the diminished functioning of organs.
The notion of accumulated damage was first introduced in 1882 by biologist Dr. August Weismann as the "wear and tear" theory.
Wearing of the body can be attributable to internal or external causes that eventually lead to an accumulation of insults which surpasses the capacity for repair.
Due to these internal and external insults, cells lose their ability to regenerate, which ultimately leads to mechanical and chemical exhaustion.
[15] Mutation accumulation theory was first proposed by Peter Medawar in 1952[13] as an evolutionary explanation for biological ageing and the associated decline in fitness that accompanies it.
Medawar posited that over time these mutations would accumulate due to genetic drift and lead to the evolution of what is now referred to as ageing.
[18] The idea that free radicals are toxic agents was first proposed by Rebeca Gerschman and colleagues in 1945,[19] but came to prominence in 1956, when Denham Harman proposed the free-radical theory of aging and even demonstrated that free radical reactions contribute to the degradation of biological systems.
One hypothesis proposed by physicist Gioacchino Failla in 1958 is that damage accumulation to the DNA causes aging.
The first experimental test of this idea was by Hart and Setlow[31] who measured the capacity of cells from seven different mammalian species to carry out DNA repair.
In general, the findings of these studies indicated a good correlation between nucleotide excision repair capacity and life span.
Further support for the theory that DNA damage is the primary cause of aging comes from study of Poly ADP ribose polymerases (PARPs).
[33] The life span of 13 mammalian species correlated with poly(ADP ribosyl)ation capability measured in mononuclear cells.
Crosslinking of DNA can induce replication errors, and this leads to deformed cells and increases the risk of cancer.
The epigenetic clock, which relatively objectively measures the biological age of cells, are useful tool for testing different anti-aging approaches.
[18] Walford, who stated that his optimized health regime would allow him to live to 120, died of amytrophic lateral sclerosis at age 79. attribution contains material copied from Gerontology.