Biometal (biology)
Modern advancements in analytical technology have made it clear the importance of biometals in signalling pathways and the initial thoughts on the chemical basis of life.
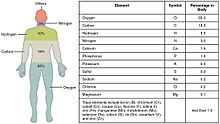
The list is not exhaustive, because it covers only the principal class members; others that are trace metals of especially low bioconcentration are not explored herein.
The body is made up of approximate 1.5% calcium and this abundance is reflected in its lack of redox toxicity and its participation in the structure stability of membranes and other biomolecules.
[7] In phosphorylating enzymes like ATPase or kinases and phosphates, magnesium acts as a stabilizing ion in polyphosphate compounds due its Lewis acidity.
In vitro, the concentration of free magnesium acts as a strict regulator and stabilizer for the enzyme activity of V-PPiase.
[6] Manganese plays a significant role in host defense, blood clotting, reproduction, digestion and various other functions in the body.
In particular, when concerning host defense, manganese acts as a preventative measure for oxidative stress by destroying free radicals which are ions that have an unpaired electron in their outer shells.
In humans, zinc is primarily found in various organs and tissues such as the brain, intestines, pancreas and mammary glands.
It plays an important role in maintenance of the cell membrane potential and the electrochemical gradient in the body via the sodium-potassium pump and sodium-glucose transport proteins.
Sodium also serves a purpose in the nervous system and cell communication as they flood into axons during an action potential to preserve the strength of the signal.
[12] Iron is also the most abundant transition metal in the human body and it is used in various processes like oxygen transport and ATP production.
Ferric ions can be reduced via superoxide and the product can be reoxidized via peroxide to form hydroxyl radicals.
Hydroxyl radicals and other reactive oxygen species when generated near DNA can cause point mutations, cross-linkage and breaks.
[15] The third way it can act as a carcinogen is by functioning as an essential nutrient for unrestricted proliferation of tumor cells.
Lithium salts have proven to be useful as a mood stabilizer and antidepressant in the treatment of mental illness such as bipolar disorder.
[18] For example, arsenic works as a potent poison due to its effects as an enzyme inhibitor, disrupting ATP production.
[21] On the other hand, Ni–Ti–Cu wires are used for artificial heart muscles[22] and iron and gold particles can guide magnetic drug delivery or destroy tumor cells.
[22] Bigger biometal structures (relying on metallic elements and alloys) in medicine can be classified into three types: fibre, bulk scaffolds, and nanotubes.