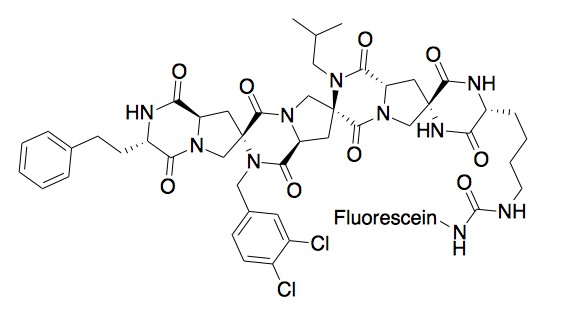
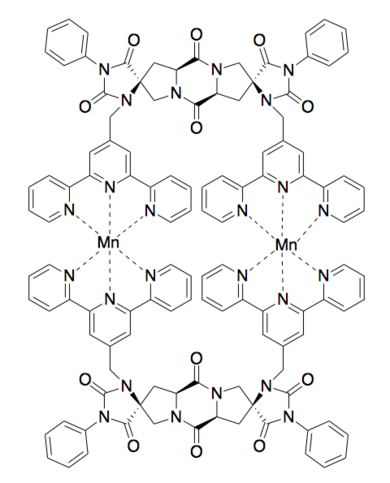
Spiroligomer
Spiroligomer molecules (also known as bis-peptides) are synthetic oligomers made by coupling pairs of bis-amino acids into a fused ring system.
[1] Spiroligomer molecules are rich in stereochemistry and functionality because of the variety of bis-amino acids that are capable of being incorporated during synthesis.
[2] Due to the rigidity of the fused ring system,[3] the three-dimensional shape of a Spiroligomer molecule – as well as the display of any functional groups – can be predicted, allowing for molecular modeling and dynamics.
Spiroligomer molecules are synthesized in a step-wise approach by adding a single bis-amino acid at each stage of the synthesis.
[7] The second Spiroligomer catalyst accelerated an aromatic Claisen rearrangement with a catalytic dyad similar to that found in ketosteroid isomerase.