Boron carbide
Boron carbide (chemical formula approximately B4C) is an extremely hard boron–carbon ceramic, a covalent material used in tank armor, bulletproof vests, engine sabotage powders,[2] as well as numerous industrial applications.
[3] Boron carbide was discovered in the 19th century as a by-product of reactions involving metal borides, but its chemical formula was unknown.
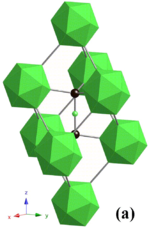
This structure is layered: the B12 icosahedra and bridging carbons form a network plane that spreads parallel to the c-plane and stacks along the c-axis.
[18] Nuclear applications of boron carbide include shielding and reaction regulation (control rod).
[11] Boron carbide filaments exhibit auspicious prospects as reinforcement elements in resin and metal composites, attributed to their exceptional strength, elastic modulus, and low density characteristics.
[19] In addition, boron carbide filaments are not affected by radiation due to its ability to absorb neutrons.