Brain cell
[2] Neurons are often grouped into a cluster known as a nucleus where they usually have roughly similar connections and functions.
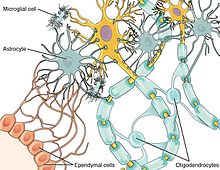
Glia are grouped into macroglia –astrocytes, ependymal cells, and oligodendrocytes, and much smaller microglia which are the macrophages of the central nervous system.
Astrocytes are seen to be capable of communication with neurons involving a signalling process similar to neurotransmission - called gliotransmission.
[1] Neurons are polarised cells that are specialised for the conduction of action potentials also called nerve impulses.
Cortical interneurons vary in shape, molecular make-up, and electrophysiology; they function collectively to maintain the balance between excitation and inhibition in the cortex primarily through the use of GABA.
Disruption of this balance is a common feature of neuropsychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia.