British Columbia
[18] Major sectors of British Columbia's economy include forestry, mining, filmmaking and video production, tourism, real estate, construction, wholesale, and retail.
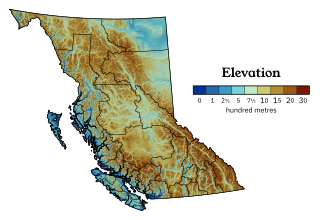
[29] The Coast Mountains and the Inside Passage's many inlets provide some of British Columbia's renowned and spectacular scenery, which forms the backdrop and context for a growing outdoor adventure and ecotourism industry.
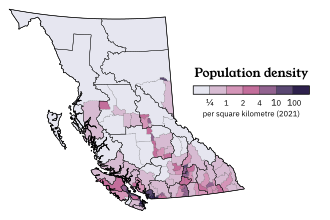
The northern, mostly mountainous, two-thirds of the province is largely unpopulated and undeveloped, except for the area east of the Rockies, where the Peace River Country contains BC's portion of the Canadian Prairies, centred at the city of Dawson Creek.
British Columbia is considered part of the Pacific Northwest and the Cascadia bioregion, along with the American states of Alaska, Idaho, (western) Montana, Oregon, Washington, and (northern) California.
Atlin in the province's far northwest, along with the adjoining Southern Lakes region of Yukon, get midwinter thaws caused by the Chinook effect, which is also common (and much warmer) in more southerly parts of the Interior.
[52] These peoples developed complex cultures dependent on the western red cedar that included wooden houses, seagoing whaling and war canoes and elaborately carved potlatch items and totem poles.
Colonies originally begun with the support of the Hudson's Bay Company (Vancouver Island, the mainland) were amalgamated, then entered Confederation as British Columbia in 1871 as part of the Dominion of Canada.
In 1793, Alexander Mackenzie was the first European to journey across North America overland to the Pacific Ocean, inscribing a stone marking his accomplishment on the shoreline of Dean Channel near Bella Coola.
His expedition theoretically established British sovereignty inland, and a succession of other fur company explorers charted the maze of rivers and mountain ranges between the Canadian Prairies and the Pacific.
The northeast corner of the province east of the Rockies, known as the Peace River Block, was attached to the much larger Athabasca District, headquartered in Fort Chipewyan, in present-day Alberta.
All that was changed with the westward extension of American exploration and the concomitant overlapping claims of territorial sovereignty, especially in the southern Columbia Basin (within present day Washington and Oregon).
New Caledonia, as the whole of the mainland rather than just its north-central Interior came to be called, continued to be an unorganized territory of British North America, "administered" by individual HBC trading post managers.
[62]: 26 He was also struck by the majestic beauty of the site, writing in his letter to Blackwood, The entrance to the Frazer is very striking—Extending miles to the right & left are low marsh lands (apparently of very rich qualities) & yet fr the Background of Superb Mountains-- Swiss in outline, dark in woods, grandly towering into the clouds there is a sublimity that deeply impresses you.
By the time of this gold rush, the character of the colony was changing, as a more stable population of British colonists settled in the region, establishing businesses, opening sawmills, and engaging in fishing and agriculture.
With this increased stability, objections to the colony's absentee governor and the lack of responsible government began to be vocalized, led by the influential editor of the New Westminster British Columbian and future premier, John Robson.
The influx of a non-European population stimulated resentment from the dominant ethnic groups, resulting in agitation and an attempt to restrict the ability of Asian people to immigrate to British Columbia through the imposition of the Chinese head tax.
His management style, implementation of the Harmonized Sales Tax (HST) despite election promises not to introduce it, and cancellation of the BC Rail corruption trial[disputed – discuss] led to low approval ratings and loss of caucus support: he resigned in November 2010.
Early Clark government actions included raising the minimum wage, creating a new statutory holiday in February called "Family Day", and pushing the development of BC's liquefied natural gas industry.
While the coast of British Columbia and some valleys in the south-central part of the province have mild weather, the majority of its land mass experiences a cold-winter-temperate climate similar to the rest of Canada.
[95] The economic history of British Columbia is replete with tales of dramatic upswings and downswings, and this boom and bust pattern has influenced the politics, culture and business climate of the province.
A variety of scandals plagued the 2001–2017 Liberal government, including Premier Gordon Campbell's arrest for drunk driving in Maui and the resignation of various cabinet ministers because of conflict-of-interest allegations.
Campbell eventually resigned in late 2010 due to opposition to his government's plan to introduce a Harmonized Sales Tax (HST) and was replaced by Christy Clark as premier in the 2011 BC Liberal leadership election.
A couple of busy intercity corridors outside Greater Vancouver feature more heavily signalized limited-mobility arterial highways that are mostly four-lane and often divided by portable median traffic barriers.
Signalization along both these highways is heaviest through urban areas and along inter-urban sections where traffic volumes are similar to and sometimes higher than the freeways, but where funding is not available for upgrades to interchanges or construction of high-mobility alternative routes or bypasses.
[119] Rail development expanded greatly in the decades after the Canadian Pacific Railway was completed, in 1885, and was the chief mode of long-distance surface transportation until the expansion and improvement of the provincial highways system began in the 1950s.
Traditional Indigenous art of the Pacific Northwest is typically distinguished by the formline style, which is defined as "continuous, flowing, curvilinear lines that turn, swell and diminish in a prescribed manner.
Notable English-Canadian artists of 19th and early 20th century British Columbia include architect Francis Rattenbury, designer James Blomfield, and painter Emily Carr.
Vancouver's art scene was dominated by lyrical abstraction and surrealist landscape painting in the mid-20th century through such artists as B. C. Binning, Jack Shadbolt, Gordon A. Smith, Takao Tanabe, Don Jarvis, and Toni Onley.
This school is generally considered to include artists Jeff Wall, Ian Wallace, Ken Lum, Roy Arden, Stan Douglas, and Rodney Graham.
Some important popular music acts include bands such as Spirit of the West, Theory of a Deadman, Trooper, Gob, and The New Pornographers, and solo artists such as Bryan Adams, Carly Rae Jepsen, Mac DeMarco, Michael Bublé, Nelly Furtado, and Diana Krall.