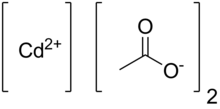
Cadmium acetate
Cadmium acetate is the chemical compound with the formula Cd(O2CCH3)2(H2O)2.
The compound is marketed both as the anhydrous form and as a dihydrate, both of which are white or colorless.
It forms by treating cadmium oxide with acetic acid:[3][4] It can also be prepared by treating cadmium nitrate with acetic anhydride.
[7] It is a coordination polymer, featuring acetate ligands interconnecting cadmium centers.
Cadmium compounds are considered Group 1 carcinogens by the IARC.