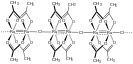
Ruthenium(III) acetate
A representative derivative is the dihydrate of the tetrafluoroborate salt [Ru3O(O2CCH3)6(OH2)3]BF4(H2O)2, which is the source of the data in the table above.
[2] This and related salts are forest green, air-stable solids that are soluble in alcohols.
The same structure is shared with basic acetates of iron, chromium, iridium, and manganese.
[3] The basic acetates of ruthenium were reported in the early 1950s but were not properly formulated.
[4] Basic ruthenium acetate reacts with many ligands such as triphenylphosphine and pyridine concomitant with reduction.