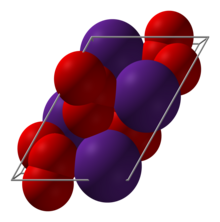
Caesium ozonide
It consists of caesium cations Cs+ and ozonide anions O−3.
It can be formed by reacting ozone with caesium superoxide:[2][3] The compound reacts strongly with any water in the air forming caesium hydroxide.
[3] In fact, the compound is metastable to decomposition into caesium superoxide, slowly decomposing at room temperature, but can remain intact for months if stored at −20 °C.
[4] Above around 8 °C, the crystal structure is of the caesium chloride type, with the ozonide ion in place of the chloride ion.
At lower temperatures, the crystal structure changes to a structure identical to rubidium ozonide (RbO3), with space group P21/c.