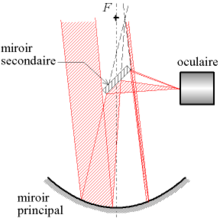
Catoptrics
Catoptrics (from Ancient Greek: κατοπτρικός katoptrikós, "specular",[1] from Ancient Greek: κάτοπτρον katoptron "mirror"[2]) deals with the phenomena of reflected light and image-forming optical systems using mirrors.
Catoptrics is the title of two texts from ancient Greece: The Latin translation of Alhazen's (Ibn al-Haytham) main work, Book of Optics (Kitab al-Manazir),[6] exerted a great influence on Western science: for example, on the work of Roger Bacon, who cites him by name.
He made the observation that the ratio between the angle of incidence and refraction does not remain constant, and investigated the magnifying power of a lens.
[8] Alhazen's work influenced Averroes' writings on optics,[citation needed] and his legacy was further advanced through the 'reforming' of his Optics by Persian scientist Kamal al-Din al-Farisi (d. ca.
1320) in the latter's Kitab Tanqih al-Manazir (The Revision of [Ibn al-Haytham's] Optics).