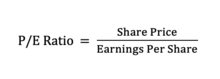Class B share
[4] There are also different reasons for creating Class B shares within a company—there are, however, similar arrangements which companies seem to use when it comes to equity structure.
[5] Class B common shares can be invested in through mutual funds, or through the public market (stock exchange).
[8] Class B shares are financial instruments which represent ownership in a company and proportionate claims on its assets.
Additionally, stocks traded OTC usually belong to smaller companies which do not have the resources to be listed on formal exchanges.
[18] Additionally, unequal voting shares are created so that owners of the company do not have to give up control, but can still tap into the public equity market for financing.
[19] Furthermore, the price of the new Class B shares attracted many small investors, whilst making Berkshire accessible to the people with modest amounts of capital.
[20] Additionally, his intention was to market Class B shares as a type of long-term investment to prevent prices from fluctuating from supply concerns.
[17] Mr Buffett also refused to a stock split and claimed that the high price of Class A shares created an intentional barrier to entry.
It is represented by the stock price divided by the company’s most recent earnings per share (EPS).
[27] It evaluates the company’s financial leverage by dividing total liabilities by shareholder equity.
It also gives insight on the ability of shareholder equity to cover outstanding debt in case the business fails.
[29] Additionally, when the D/E ratio gets too high, the cost of borrowing is dramatically increased which may eventually drive down the Class B’s share price of the firm.
However, it may also be good as it shows that a firm can easily repay its debt obligations and is using leverage to increase the amount of equity returns.
The percentage difference in voting rights depends on how the company wishes to structure its stock.
[31] The purpose of this structure is argued to ensure stability of the company and prevent the board and management from feeling short-term pressure, which in turn allows them to focus on long-term goals.
Although these Class A shares are publicly owned and traded on the market, they are generally out of reach for the typical investor.
This means that when the investor chooses to sell, a percentage of the dollar value of shares sold has to be paid.
This back-end load, however, decreases directly proportional to the holding period of the fund,[36] and is eventually eliminated.
[37] Class B mutual fund shares are seen to be a good investment if investors have less cash and a longer time horizon.
[38][39] Companies choose to mitigate the risk of exposing their governance and assets to the public market by defining different classes of shares to ensure corporate insiders are in control of the voting rights.
They use different classifications to address issues such as voting authority, dividends, as well as rights to capital and assets.
Mark Zuckerberg, the CEO of Meta, owns 360 million Class B shares which gives him complete voting power over other shareholders.
The Executive Chairman of Alibaba Group, Jack Ma, has added that his company’s voting structure aims to preserve the firm’s culture whilst avoiding short-term behaviour at the expense of long-term development.
[46] Google had similar intentions in releasing their Class B shares to make it harder for the public to influence the company’s strategic decisions through their voting rights.
On the other hand, Google's Class B stock, which is owned and split amongst CEO Eric Schmidt and founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin, was created to have 10 votes per share.
[47] Google’s CEO said that the purpose of creating Class B shares was to make it easier for management to follow a “long-term, innovation-based growth strategy”.
[49] After approving the resolution, the company will have to submit a form to the regulatory authority in the country, where the process is given full validation.