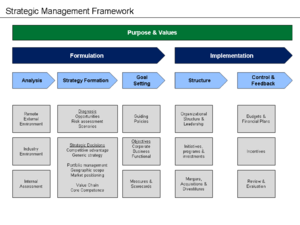
Strategic planning
It is executed by strategic planners or strategists, who involve many parties and research sources in their analysis of the organization and its relationship to the environment in which it competes.
Strategy can be planned (intended) or can be observed as a pattern of activity (emergent) as the organization adapts to its environment or competes in the market.
The commitment of top management must be evident throughout the process to reduce resistance to change, ensure acceptance, and avoid common pitfalls.
We are already in a transitional period in which old practices are no longer permanent but require revision to meet the needs of academia, which is frustrating in the educational sector.
Instead of defining the vision for how we want our children to live, they direct their attention to courses, content, and resources with the mistaken belief that societally useful outcomes will follow.
Data is gathered from various sources, such as interviews with key executives, review of publicly available documents on the competition or market, primary research (e.g., visiting or observing competitor places of business or comparing prices), industry studies, reports of the organization's performance, etc.
Inputs are gathered to help establish a baseline, support an understanding of the competitive environment and its opportunities and risks.
[10] The strategy may include a diagnosis of the competitive situation, a guiding policy for achieving the organization's goals, and specific action plans to be implemented.
Capital budgets very often form the backbone of a strategic plan, especially as it increasingly relates to Information and Communications Technology (ICT).
McKinsey & Company developed a capability maturity model in the 1970s to describe the sophistication of planning processes, with strategic management ranked the highest.
[13] For Michael C. Sekora, Project Socrates founder in the Reagan White House, during the cold war the economically challenged Soviet Union was able to keep on western military capabilities by using technology-based planning while the U.S. was slowed by finance-based planning, until the Reagan administration launched the Socrates Project, which should be revived to keep up with China as an emerging superpower.
In a 2019 meta-analysis including data from almost 9,000 public and private organizations, strategic planning is found to have a positive impact on organizational performance.
The plans are the prime media communicating the management's strategic intentions, thereby promoting a common direction instead of individual discretion.
Hence, they posit that strategic plan is a genre of organizational communication (Bhatia, 2004; Yates and Orlikowski, 1992 as cited in Cornut et al., 2012).
[17] In this sense, genre is defined as the "conventionalized discursive actions in which participating individuals or institutions have shared perceptions of communicative purposes as well as those of constraints operating their construction, interpretation and conditions of use" (Bhatia, 2004: 87; see also Frow, 2005; Swales, 1990 as cited in Cornut et al., 2012).
This included annual reports from the public sector and nongovernment organizations, research articles, project plans, executive speeches, State of the Union addresses, horoscopes, religious sermons, business magazine articles and annual reports for-profit corporations included in the Standard & Poor's 500 largest companies (S&P 500).
The book edited by Mandeville-Gamble (2015) sees the roles of managers as important in terms of communicating the strategic vision of the organization.
[19] Many of the authors in the book by Mandeville-Gamble agree that a strategic plan is merely an unrealized vision unless it is widely shared and sparks the willingness to change within individuals in the organization.
Similarly, Goodman in 2017[20] emphasized that the advent of the internet and social media has become one of the most important vehicle to which corporate strategic plan can be distributed to an organizations internal and external stakeholders.
Strategic planning through control mechanisms (mostly by the way of a communication program) is set in the hopes of coming to desired outcomes that reflect company or organizational goals.
Strategic planning is both the impetus for and result of critical thinking, optimization, and motivation for the growth and development of organizations.
The core disciplines, which are inherent in systems thinking, personal and organizational mastery, mental models, building a shared vision, and team learning.