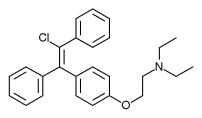
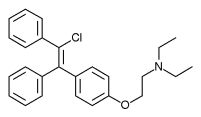
Clomifene
active metabolites: 4-OH-CLO : 13–34 hrs[2] Clomifene, also known as clomiphene, is a medication used to treat infertility in women who do not ovulate, including those with polycystic ovary syndrome.
[5] Other side effects can include changes in vision, vomiting, trouble sleeping, ovarian cancer, and seizures.
[10] Clomifene (particularly the purified enclomiphene isomer) has also been found to have a powerful ability to boost or restore testosterone levels in hypogonadal men.
[17][non-primary source needed] It has been found to increase testosterone levels by 2–2.5 times in hypogonadal men at such dosages.
[17][18] Despite the use of questionnaires in testosterone replacement comparator trials being called into question, clomifene's lower cost, therapeutic benefits, and greater value towards hypogonadism improvement have been noted.
Zuclomifene has pro-estrogenic properties, whereas enclomifene is pro-androgenic, i.e. it promotes testosterone production through stimulation of the HPG axis.
[25] Because clomifene can enhance egg production in hens, athletes may inadvertently consume the substance through contaminated food.
[7] Less common effects (1–10% of people) include visual symptoms (blurred vision, double vision, floaters, eye sensitivity to light, scotomata), headaches, vasomotor flushes (or hot flashes), light sensitivity and pupil constriction, abnormal uterine bleeding and/or abdominal discomfort.
[7] Rare adverse events (<1% of people) include: high blood level of triglycerides, liver inflammation, reversible baldness and/or ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
[35] Clomifene is a prodrug being activated via similar metabolic pathways as the related triphenylethylene SERMs tamoxifen and toremifene.
[medical citation needed] In normal physiologic female hormonal cycling, at seven days past ovulation, high levels of estrogen and progesterone produced from the corpus luteum inhibit GnRH, FSH, and LH at the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary.
[medical citation needed] If fertilization does not occur in the post-ovulation period the corpus luteum disintegrates due to a lack of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
[medical citation needed] This would normally be produced by the embryo in the effort of maintaining progesterone and estrogen levels during pregnancy.
[medical citation needed] In the presence of clomifene, the body perceives a low level of estrogen, similar to day 22 in the previous cycle.
[medical citation needed] Since estrogen can no longer effectively exert negative feedback on the hypothalamus, GnRH secretion becomes more rapidly pulsatile, which results in increased pituitary gonadotropin release.
[medical citation needed] (More rapid, lower amplitude pulses of GnRH lead to increased LH and FSH secretion, while more irregular, larger amplitude pulses of GnRH leads to a decrease in the ratio of LH to FSH.
[44][45] Concerns about possible induction of desmosterolosis and associated symptoms such as cataracts and ichthyosis with extended exposure precluded the use of clomifene in the treatment of breast cancer.
[2] Primarily due to differences in CYP2D6 genetics, steady state concentrations and individual response to clomifene are highly variable.
[4] A team at William S. Merrell Chemical Company led by Frank Palopoli synthesized clomifene in 1956; after its biological activity was confirmed a patent was filed and issued in November 1959.
[10] Clomifene was studied in the treatment of advanced breast cancer during the period of 1964 to 1974 and was found to be effective but was abandoned due to concerns about desmosterolosis with extended use.
[62] Clomifene is marketed under many brand names worldwide, including Beclom, Bemot, Biogen, Blesifen, Chloramiphene, Clofert, Clomene, ClomHEXAL, Clomi, Clomid, Clomidac, Clomifen, Clomifencitrat, Clomifene, Clomifène, Clomifene citrate, Clomifeni citras, Clomifeno, Clomifert, Clomihexal, Clomiphen, Clomiphene, Clomiphene Citrate, Cloninn, Clostil, Clostilbegyt, Clovertil, Clovul, Dipthen, Dufine, Duinum, Fensipros, Fertab, Fertec, Fertex, Ferticlo, Fertil, Fertilan, Fertilphen, Fertin, Fertomid, Ferton, Fertotab, Fertyl, Fetrop, Folistim, Genoclom, Genozym, Hete, I-Clom, Ikaclomin, Klofit, Klomen, Klomifen, Lomifen, MER 41, Milophene, Ofertil, Omifin, Ova-mit, Ovamit, Ovinum, Ovipreg, Ovofar, Ovuclon, Ovulet, Pergotime, Pinfetil, Profertil, Prolifen, Provula, Reomen, Serofene, Serophene, Serpafar, Serpafar, Surole, Tocofeno, and Zimaquin.
[64] Clomifene was studied for treatment and prevention of breast cancer, but issues with toxicity led to abandonment of this indication, as did the discovery of tamoxifen.
[65] Like the structurally related drug triparanol, clomifene is known to inhibit the enzyme 24-dehydrocholesterol reductase and increase circulating desmosterol levels, making it unfavorable for extended use in breast cancer due to risk of side effects like irreversible cataracts.