Conceptual graph
In the first published paper on CGs, John F. Sowa used them to represent the conceptual schemas used in database systems.
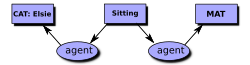
[2] In this approach, a formula in first-order logic (predicate calculus) is represented by a labeled graph.
In CGIF, this CG would be represented by the following statement: [Cat Elsie] [Sitting *x] [Mat *y] (agent ?x Elsie) (location ?x ?y) In CGIF, brackets enclose the information inside the concept nodes, and parentheses enclose the information inside the relation nodes.
The letters x and y, which are called coreference labels, show how the concept and relation nodes are connected.
Key features of GBKR, the graph-based knowledge representation and reasoning model developed by Chein and Mugnier and the Montpellier group, can be summarized as follows:[3] COGITANT and COGUI are tools that implement the GBKR model.