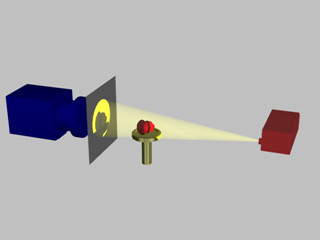
Cone beam reconstruction
[1] Cone beam reconstruction uses a 2-dimensional approach for obtaining projection data.
The scintillator converts X-ray radiation to visible light, which is picked up by the camera and recorded.
The second method involves rotating the X-ray source and camera around the object, as is done in ordinary CT scanning and SPECT imaging.
This adds complexity, size and cost to the system, but removes the need to rotate the object.
The method is referred to as cone-beam reconstruction because the X-rays are emitted from the source as a cone-shaped beam.