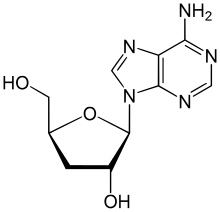
Cordycepin
Cordycepin, or 3'-deoxyadenosine, is a derivative of the nucleoside adenosine, differing from the latter by the replacement of the hydroxy group in the 3' position with a hydrogen.
[3] Cordyceps fungi produce cordycepin as a means of infecting insect populations, due to its biological activity.
It can therefore participate in certain biochemical reactions (for example, 3-dA can trigger the premature termination of mRNA synthesis).
[5][6] By acting as an adenosine analog, cordycepin is the most potent molecular circadian clock resetter out of several screened compounds.
[15] Cordycepin has anti-inflammatory qualities,[16] as well as the ability to defend against injury from cerebral ischemia in mice.