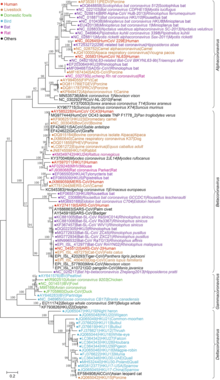
Coronaviridae
Coronaviridae is a family of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect amphibians, birds, and mammals.
Commonly referred to as coronaviruses in the English language, the family coronaviridae includes the subfamilies Letovirinae and Orthocoronavirinae; the latter also known as coronavirinae.
Four human coronaviruses cause typically minor symptoms of a common cold, while three are known to cause more serious illness and can be lethal: SARS-CoV-1, which causes SARS; MERS-CoV, which causes MERS; and SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19.
[12] Symptoms vary in other species: in chickens, they cause an upper respiratory disease, while in cows and pigs coronaviruses cause diarrhea.
The genome size of coronaviruses ranges from approximately 26 to 32 kilobases, among the largest for an RNA virus (second only to a 41-kb nidovirus recently discovered in planaria).