Corpus callosum
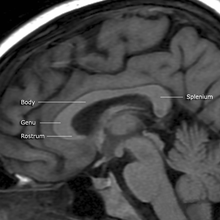
[2][3] A number of separate nerve tracts, classed as subregions of the corpus callosum, connect different parts of the hemispheres.
The lower, much thinner part is the rostrum and is connected below with the lamina terminalis, which stretches from the interventricular foramina to the recess at the base of the optic stalk.
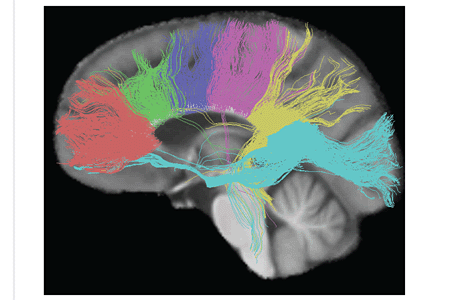
[10] The tractogram pictured shows the nerve tracts from six segments of the corpus callosum, providing linking of the cortical regions between the cerebral hemispheres.
Those of the genu are shown in coral; of the premotor, green; of the sensory-motor, purple; of the parietal, pink; of the temporal, yellow; and of the splenium, blue.
However, advanced analytical techniques of computational neuroanatomy developed in the 1990s showed that sex differences were clear, but confined to certain parts of the corpus callosum, and that they correlated with cognitive performance in certain tests.
[14] An MRI study found that the midsagittal corpus callosum cross-sectional area is, after controlling for brain size, on average, proportionately larger in females.
[16][17][18] Analysis by shape and size has also been used to study specific three-dimensional mathematical relationships with MRIs, and have found consistent and statistically significant differences between sexes.
[25] The formation of the corpus callosum begins with the first midline crossing of pioneer axons around week 12 in the prenatal development of the human,[26] or day 15 in the embryogenesis of the mouse.
[28] This is usually reserved for cases in which complex or grand mal seizures are produced by an epileptogenic focus on one side of the brain, causing an interhemispheric electrical storm.
The diagnostic work up for this procedure involves an electroencephalogram, MRI, PET scan, and evaluation by a neurologist, neurosurgeon, psychiatrist, and neuroradiologist before a partial lobotomy surgery can be considered.
ACC is usually diagnosed within the first two years of life, and may manifest as a severe syndrome in infancy or childhood, as a milder condition in young adults, or as an asymptomatic incidental finding.
Initial symptoms of ACC usually include seizures, which may be followed by feeding problems and delays in holding the head erect, sitting, standing, and walking.
Although many children with the disorder lead normal lives and have average intelligence, careful neuropsychological testing reveals subtle differences in higher cortical function compared to individuals of the same age and education without ACC.
[31] In addition to agenesis of the corpus callosum, similar conditions are hypogenesis (partial formation), dysgenesis (malformation), and hypoplasia (underdevelopment, including too thin).
[32][33] Kim Peek, a savant and the inspiration behind the movie Rain Man, was found with agenesis of the corpus callosum, as part of FG syndrome.
[38] The corpus callosum is found only in placental mammals, while it is absent in monotremes and marsupials,[39] as well as other vertebrates such as birds, reptiles, amphibians and fish.
[12] The fibrous bundle at which the corpus callosum appears can and does increase to such an extent in humans that it encroaches upon and wedges apart the hippocampal structures.