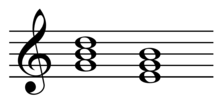
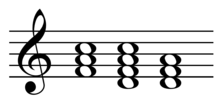
Parallel and counter parallel
Dr. Riemann...sets himself to demonstrate that every chord within the key-system has, and must have, either a Tonic, Dominant or Subdominant function or significance.
The "counter parallel" or "contrast chord" is terminology used in German theory derived mainly from Hugo Riemann to refer to (US:) relative (German: parallel) diatonic functions and is abbreviated Tcp in major and tCp in minor (Tkp respectively tKp in Riemann's diction).
According to Riemann the chord is derived through Leittonwechselklänge (German, literally: "leading-tone changing sounds"), sometimes called gegenklang or "contrast chord", abbreviated Tl in major and tL in minor,[6] or, in German literature, abbreviated Tg in major and tG in minor (standing for "Gegenklang" or "Gegenparallel")[citation needed].
A chord should be analysed as a Tcp rather than Dp or sP particularly at cadential points, for example at an interrupted cadence, where it substitutes the tonic.
It is most easily recognised in a minor key since it creates an ascending semitone step at the end of the cadence by moving from the major dominant chord to the minor counter parallel: In four-part harmony, the Tcp usually has a doubled third to avoid consecutive fifths or octaves.
Perhaps the central reason is that this ingenious, occasionally convoluted system enabled Riemann to...[interpret] ostensibly remote triads...through the traditional terms of the I-IV-V-I, or now T-S-D-T, cadential schema.