Curonian colonisation
Small, but wealthy, the Duchy took a modest part in the European colonization settlement attempts of West Africa and the Caribbean.
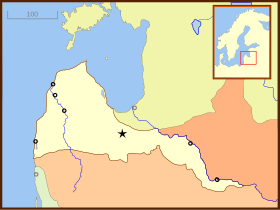
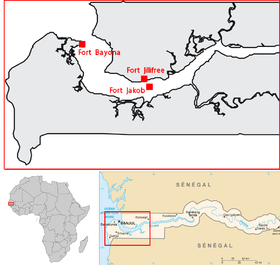
[1] The Courland and Semigallia's colonies exported sugar, tobacco, coffee, cotton, ginger, indigo, rum, cocoa, tortoise shells, as well as tropical birds and their much sought after feathers.
In the end, the Duchy would manage to retain control of these lands for less than a decade and the colonies were formally ceded to England in 1664.
The colonies were lost when Courland and Semigallia's neighbours took advantage of its weakened defences during the Northern Wars, when Jakob was held captive by the Swedish Army from 1658 to 1660.
In 1668, a Curonian ship attempted to reoccupy Fort Jacob but was driven off by the Dutch garrison stationed on the island.