List of modern great powers
Still participating in his deadly Italian conflicts, Francis I of France managed to finance expeditions to find trade routes to China or Cathay through landmass already discovered by the Spanish under Giovanni da Verrazzano.
At its height in 1812, the French Empire had 134 départements, ruled over 90 million subjects, maintained extensive military presence in Germany, Italy, Spain, and the Duchy of Warsaw, and could count Prussia, Russia and Austria as nominal allies.
In 1763, Pontiac's War broke out as a group of Indian tribes in the Great Lakes region and the Northwest (the modern American Midwest) were unhappy with the loss of congenial and friendly relations with the French and complained about being cheated by the new British monopoly on trade.
[35] In response, King George III issued the Royal Proclamation of 1763, which forbade white settlement beyond the crest of the Appalachians, with the hope of appeasing the Indians and preventing further insurrection, but this led to considerable outrage in the Thirteen Colonies, whose inhabitants were eager to acquire native lands.
Empresses Elizabeth and Catherine the Great presided over a golden age; in the late 17th century, they expanded the state by conquest, colonization, and diplomacy, while continuing Peter I's policy of modernization along Western European lines.
[46] Potential factors contributing to this decline include a protracted period of misrule by weak Sultans; stifled innovation and research due to growing religious and intellectual conservatism; public or military opposition to reform; or simply a need to transform the country in order for it to survive, which could have hampered all efforts to strengthen the state itself.
Even then, it was too late: much of the decline took place in the 19th century under pressure from Russia and various other powers, beginning with the Greek War of Independence, and culminating in 1875 in the Great Eastern Crisis: by 1882, the Empire had lost effective control of Egypt, Tunisia, and more.
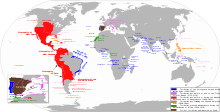
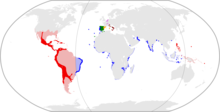
However, Spain maintained and enlarged its vast overseas empire until the 19th century, when the shock of the Peninsular War sparked declarations of independence in Quito, Venezuela, Paraguay and many more successive revolutions that split away its territories from its American mainland.
It was a country of religious freedom, confirmed by the Warsaw Confederation, one of the first European acts of its kind, which encouraged an influx of immigrants, including Armenian, Czech,[64] Dutch, French, Greek, Jewish, and Scottish.
[103] By the middle of the 17th century, the Dutch had overtaken Portugal as the dominant player in the spice and silk trade, and in 1652 founded a colony at Cape Town on the coast of South Africa, as a way-station for its ships on the route between Europe and Asia.
After the first settlers spread out around the Company station, nomadic white livestock farmers, or Trekboers, moved more widely afield, leaving the richer, but limited, farming lands of the coast for the drier interior tableland.
In their search for new trade passages between Asia and Europe, Dutch navigators explored and charted distant regions such as Australia, New Zealand, Tasmania, and parts of the eastern coast of North America.
[113] As a result of acquiring territories seized from Russia and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, as well as its involvement in the Thirty Years' War, Sweden found itself transformed into the leading power of the Baltic Sea[114] and the leader of Protestantism.
After the death of the first Soviet leader, Vladimir Lenin, in 1924, Joseph Stalin eventually won a power struggle and led the country through a large-scale industrialization with a command economy and political repression.
Sometimes also called "the Soviet Empire", it exercised its hegemony in Central and Eastern Europe and worldwide with military and economic strength, proxy conflicts and influence in developing countries and funding of scientific research, especially in space technology and weaponry.
Founded in 1776 by thirteen coastal colonies that declared their independence from Great Britain, the United States began its western expansion following the end of the American Revolutionary War and the recognition of U.S. sovereignty in the 1783 Treaty of Paris.
[160] An elaborate bureaucracy was created to regulate imports of raw materials and finished goods with the intention of eliminating foreign competition in the German marketplace and improving the nation's balance of payments.
[161] As the market was experiencing a glut and prices for petroleum were low, in 1933 the Nazi government made a profit-sharing agreement with IG Farben, guaranteeing them a 5 per cent return on capital invested in their synthetic oil plant at Leuna.
[163] Major public works projects financed with deficit spending included the construction of a network of Autobahnen and providing funding for programmes initiated by the previous government for housing and agricultural improvements.
[165] On the condition that the wife would leave the workforce, a loan of up to 1,000 Reichsmarks could be accessed by young couples of Aryan descent who intended to marry, and the amount that had to be repaid was reduced by 25 per cent for each child born.
[175] In addition to calling for the rapid construction of steel mills, synthetic rubber plants, and other factories, Göring instituted wage and price controls and restricted the issuance of stock dividends.
Its eighteen integral regions (five of which are overseas) span a combined area of 643,801 km2 (248,573 sq mi) and over 68 million people (as of December 2024[update]), making it the largest and second-most populous country in the European Union.
Under the doctrine of Dirigisme, the government historically played a major role in the economy; policies such as indicative planning and nationalisation are credited for contributing to three decades of unprecedented postwar economic growth known as Trente Glorieuses.
[283] A mixed opinion has been offered by Matthew Fleischer of the Los Angeles Times: he contends that Russia will not become a superpower unless climate change eats away at the permafrost that covers, as of March 2014, two-thirds of the country's landmass.
The absence of this permafrost would reveal immense stores of oil, natural gas, and precious minerals, as well as potential farmland, which would allow Russia to "become the world's bread basket—and control the planet's food supply".
[287][288][289] Since the creation of the Wagner Group in 2014, Russia has used it to intervene in various conflicts (while maintaining plausible deniability) in Africa aside from being involved in Libya, Syria, and even Venezuela by projecting power far away from the borders of the former Soviet Union.
Italy is a key player in maintaining international security, especially in the wider Mediterranean region,[note 1] by performing air policing duties for its allies and commanding multinational forces in foreign countries.
The source of many inventions and discoveries, the country has long been a global centre of art, music, literature, philosophy, science and technology, and fashion, and has greatly influenced and contributed to diverse fields including cinema, cuisine, sports, jurisprudence, banking, and business.
'"[368] Though Lee believes China is genuinely interested in growing within the global framework the United States has created, it is biding its time until it becomes strong enough to successfully redefine the prevailing political and economic order.
The United States is seen as a declining superpower, as indicated by factors such as poor economic recovery, financial disorder, high deficits, increasing political polarization, and overregulation forcing jobs overseas in China.