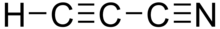Cyanoacetylene
Cyanoacetylene is an organic compound with the formula C3HN or H−C≡C−C≡N.
It is the simplest cyanopolyyne.
Cyanoacetylene has been detected by spectroscopic methods in interstellar clouds,[2] in the coma of comet Hale–Bopp and in the atmosphere of Saturn's moon Titan,[3] where it sometimes forms expansive fog-like clouds.
[4] Cyanoacetylene is one of the molecules that was produced in the Miller–Urey experiment.
[5]