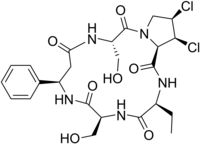
Cyclochlorotine
Cyclochlorotine[1] (CC), also known as islanditoxin,[2] is a mycotoxin produced by the fungus Penicillium islandicum[3] that causes liver damage and has carcinogenic properties.
[5] Structurally, the only thing that differentiates cyclochlorotine from the plant-derived astins of Aster tataricus, is replacement of a serine with a second 2-aminobutyrate.
[6] Cyclochlorotine is one of the toxins usually found in foods in grains such as rice, wheat, soybeans, peanuts, beans, bread, flour, etc.
Such foods serve as medium for the growth of molds such as Penicillium islandicum which in turn release toxins such as cyclochlorotine.
[7] Research shows that that biosynthesis of cyclochlorotine is a multi-step mechanism and makes use of a vital component in the last step known as NRPS (CctN).