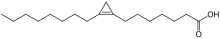
Cyclopropane fatty acid
[1] Although they are usually rare, the seed oil from lychee contains nearly 40% CPAs in the form of triglycerides.
CPAs are derived from unsaturated fatty acids by cyclopropanation.
The methylene donor is a methyl group on S-adenosylmethionine (SAM).
[3] The mechanism is proposed to involve transfer of a CH3+ group from SAM to the alkene, followed by deprotonation of the newly attached methyl group and ring closure.
The cyclopropene ring is destroyed during refining and hydrogenation of the oils.