Demographics of Albania
The total population residing in Albania in September 2023 was 2,402,113 according to the most recent INSTAT census.
Maddison from 2001, estimates that in Albania about 200,000 people lived up to the year 1600, and that the population grew to 300,000 by 1700, implying an annual average growth rate of 0.4% in that period.
The growth strained economic resources during communism in a Malthusian fashion that led to the collapse of the regime and the emigration of about 20 to 25 percent of the population in the following two decades.
Albania experienced a demographic transition starting from 1960s, when crude birth rates began a slow decline, despite a government policy that called for a population increase.
There were also those who preferred not to answer (10.17%), The main ethnic groups in Albania are Albanians (91%), Greeks (1%), Egyptians (0.5%), Romani people (0.4%), Bulgarians (0.3%), as well as Bosniaks, Aromanians, Macedonians, Serbs and Montenegrins.
[9] Albanian demographics are difficult to ascertain and verify due to political corruption at the local and central level as noted by the Council of Europe.
Large scale emigration and fertility decline are supposed to be the main causes of the observed population decrease.
This figure is based on the number of dwellings for which a refusal was recorded and is included in the total population.
The 2011 census is regarded as unreliable and inaccurate by the Council of Europe, showing incompatibility with the protection of national minorities.
[19] The religious affiliation of the population was 56.7% Muslims, 13.79% undeclared, 10.03% Catholics, 6.75% Orthodox believers, 5.49% other, 2.5% Atheists, 2.09% Bektashis and 0.14% other Christians.
According to the Institute of Statistics (INSTAT), the three largest counties account for half of the population.
Over 1 million people live in Tirana and Durrës, making it the largest urban area in Albania.
[22] The area of the capital Tirana, is one of largest cities in the Balkan Peninsula and ranks 7th with a population about 800,000.
The Institute of Statistics forecast that the population may even increase by less than a fifth from 763.560 by 2011 to 909.252 by 2031, depending on the actual birth rate and the level of net migration.
These include Aromanians, Balkan Egyptians, Greeks, Bulgarians, Bosniaks, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs, and Roma.
However this census was deemed unreliable by internal and external organisations, including the Council of Europe and many of Albania's ethnic minority groups.
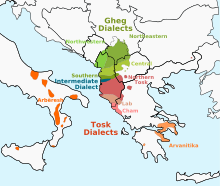
[57] Macedonians mostly live in Mala Prespa and the regions along the Macedonian border, known as 'Golo Brdo' and 'Gora'.2 The Bulgarian minority was only recognised in 2017,[58] after decades-long blockade by former Yugoslavia and following a 2016 recommendation by the European Parliament that the rights of people of Bulgarian ethnicity in the Prespa, Gollobordë, and Gora regions should be respected.
[1] The Constitution of Albania extends freedom of religion to all citizens and the government generally respects this right in practice.
However, the predominant religious communities enjoy a greater degree of official recognition and social status based on their historical presence in the country.
All registered religious groups have the right to hold bank accounts and to own property and buildings.
Centuries-old communities speaking Albanian-based dialects can be found scattered in Greece (Arvanites), Southern Italy, Sicily and Calabria (Arbëreshë) and in Ukraine.
Language knowledge is increasing due to returning migrants, as well as new Greek and Italian communities in the country.
The ethnic minorities languages include Aromanian, Serbian, Macedonian, Bosnian, Bulgarian, Gorani, and Roma.
Students must pass the graduation exams at the end of the 9th grade in order to continue their education.
[73] Source: UN World Population Prospects[75] Albanians have established communities in many regions throughout southern Europe.
Over the last twenty years, Albania has experienced major demographic changes, having the highest population growth in Europe before the collapse of communism in the country.
However, during the final days of the transition from communism to capitalism in 1990, over a million Albanians moved to foreign countries.
These include Australia, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, the Nordic countries, Switzerland and the United Kingdom.