Population decline
If a country can increase its workforce productivity faster than its population is declining, the results, in terms of its economy, the quality of life of its citizens, and the environment, can be net positive.
National efforts to confront a declining population to date have been focused on the possible negative economic consequences and have been centered on increasing the size and productivity of the workforce.
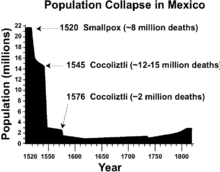
[12] Some population declines result from indeterminate causes, for example, the Bronze Age Collapse, which has been described as the worst disaster in ancient history.
[1][15] The principal cause of this phenomenon is the abrupt decline in the global total fertility rate, from 5.3 in 1963 to 2.2 in 2023, as the world continues to move through the stages of the Demographic Transition.
[1] Predictions of the net economic (and other) effects from a slow and continuous population decline (e.g. due to low fertility rates) are mainly theoretical since such a phenomenon is a relatively new and unprecedented one.
Fertility near replacement and population stability, however, would be most beneficial for standards of living when the analysis includes the effects of age structure on families as well as governments.
Fertility moderately below replacement and population decline would maximize per capita consumption when the cost of providing capital for a growing labor force is taken into account.
Since World War II, the "static" theory saw a population's absolute size as being one of the components of a country's national power.
This view holds that the quality and skill level of a labor force and the technology and resources available to it are more important than simply a nation's population size.
This negative natural population change amplified in 2022 and 2023 and, in the absence of substantial immigration, this trend will continue in the coming years due to the very low fertility rate.
[43] Its absolute total decline (9,263,000) since its peak population is the highest of all nations; this includes loss of territory and heavy net emigration.
[61] An editorial projects significant gender and age imbalance in the population in Ukraine as a substantial problem if most refugees, as in other cases, do not return over time.
Bosnia and Herzegovina's population peaked at 4,377,033 in the 1991 Census, shortly before the Yugoslav wars that produced tens of thousands of civilian victims and refugees.
The Bulgarian population has fallen by more than 844,000 people, or 11.5 percent, in the last decade, the National Institute of Statistics in Sofia said during a presentation of the results so far of the 2021 census, the first since 2011.
[85] In spite of a positive natural increase of almost 1% per year,[86] Venezuela's population has declined during the 2015-20 period due to emigration caused by threats of violence as well as shortages of basic needs.
[93] In March 2023, The Economist reported that "Over the past three years the country has lost around 2 million more people than it would ordinarily have done, as a result of war [in Ukraine], disease and exodus.
"[95] According to the analysis of economists Oleg Itskhoki and Maxim Mironov, Russia may lose more than 10% of men aged 20–29 as a result of losses in the war and emigration.
Other cities whose populations have dramatically shrunk since the 1950s include Baltimore, Buffalo, Cincinnati, Cleveland, Flint, Gary, New Orleans, St. Louis, Pittsburgh, Scranton, Youngstown and Wilmington (Delaware).
The term has more recently been applied to other migrations by whites, from older, inner suburbs to rural areas, as well as from the U.S. Northeast and Midwest to the warmer climate in the Southeast and Southwest.
[120] A combination of long-term trends, housing affordability, falling birthrates and rising death rates from the COVID-19 pandemic have caused as many as 16 US states to start declining in population.
Due to continued emigration, many departments in France are seeing declines in population, including: Aisne, Allier, Ardennes, Cantal, Charente, Cher, Corrèze, Creuse, Dordogne, Eure, Eure-et-Loir, Haute-Marne, Haute-Saône, Haute-Vienne, Indre, Jura, Loir-et-Cher, Lot-et-Garonne, Lozère, Manche, Marne, Mayenne, Meuse, Moselle, Nièvre, Orne, Paris, Sarthe, Somme, Territoire de Belfort, Vosges and Yonne.
The term 'white flight' has also been used for large-scale post-colonial emigration of whites from Africa, or parts of that continent,[122][123][124][125][126] driven by levels of violent crime and anti-colonial state policies.
[130] The Parsis of India have one of the lowest fertility rates in the world (0.8 children per woman in 2017); this coupled with emigration has resulted in population decline at least since the 1940s.
Regionally, the mountainous and Christian-majority areas have low fertility rates comparable to European nations, with most of the population increase being concentrated in northern Lebanon.
[134] A country with a declining population will struggle to fund public services such as health care, old age benefits, defense, education, water and sewage infrastructure, etc.
These generally fall into three broad categories:[137] For example, Sweden built up an extensive welfare state from the 1930s and onward, partly as a consequence of the debate following "Crisis in the Population Question", published in 1934.
Under the new measure, between 260,000 and 345,000 five-year visas will be made available for workers in 14 sectors suffering severe labor shortages, including caregiving, construction, agriculture and shipbuilding.
[145] Increasing workforce productivity through intensive growth can only succeed if workers who become unemployed through the introduction of new technology can be retrained so that they can keep their skills current and not be left behind.
[147][148] A long-term population decline is typically caused by sub-replacement fertility, coupled with a net immigration rate that fails to compensate for the excess of deaths over births.
[150] The table shows UN predictions of long-term decline of population growth rates in every region; however, short-term baby booms and healthcare improvements, among other factors, can cause reversals of trends.



|
≥ 30
25 – 29.99
20 – 24.99
15 – 19.99
|
10 – 14.99
5 – 9.99
0 – 4.99
–5 – –0.01
|
< –5
Data unavailable
|


