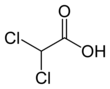
Dichloroacetic acid
[6] DCA is prepared from chloral hydrate also by the reaction with calcium carbonate and sodium cyanide in water followed by acidifying with hydrochloric acid.
[11] A randomized controlled trial in children with congenital lactic acidosis found that while DCA was well tolerated, it was ineffective in improving clinical outcomes.
In addition, clinical trial subjects were incapable of continuing on DCA as a study medication owing to progressive toxicities.
[15] Because the drug cannot be patented, financing the broad and expensive testing required to obtain FDA approval is problematic.
[16] The US Food and Drug Administration enforces the law that prohibits the sale of substances with the suggestion that they are cancer treatments unless they have been approved by the FDA.
[20] In vitro work with DCA on neuroblastomas (which have fewer recognised mitochondrial abnormalities) showed activity against malignant, undifferentiated cells.
[23] A 2018 study found that DCA could trigger a metabolic switch from glycolysis (the Warburg effect) to mitochondrial OXPHOS and increase reactive oxygen stress affecting tumor cells.
[27] On the other hand, the 2008 review in BJC [25] states "This neurotoxicity resembled the pattern of length-dependent, axonal, sensorimotor polyneuropathy without demyelination."