Dioxirane
In chemistry, dioxirane (systematically named dioxacyclopropane, also known as methylene peroxide or peroxymethane) is an organic compound with formula CH2O2.
[2] Its formation is thought to be radical in nature, preceding via a Criegee intermediate.
Microwave analysis has indicated C-H, C-O and O-O bond lengths of 1.090, 1.388 and 1.516 Å respectively.
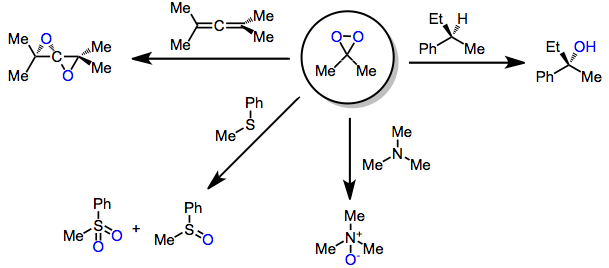
Because of their low-lying σ*O-O orbital, they are highly electrophilic oxidants and react with unsaturated functional groups, Y-H bonds (yielding oxygen insertion products), and heteroatoms.
[5] Although this class of reagents is most famous for the epoxidation of alkenes, dioxiranes have been used extensively for other kinds of oxidations as well.