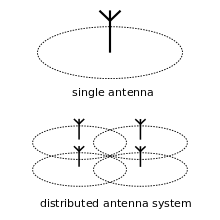
Distributed antenna system
DAS antenna elevations are generally at or below the clutter level, and node installations are compact.
DAS is often used in scenarios where alternate technologies are infeasible due to terrain or zoning challenges.
This artificially increases delay spread in areas of overlapped coverage, permitting quality improvements via time diversity.
[citation needed] Using a distributed antenna system to create an area of wireless coverage, it is possible to use this technique to propagate indoor WiFi for commercial uses.
All high-rise buildings in New York must have a dedicated wireless two-way communications system for fire department use.
[10] The Industry designs and builds DAS systems in line with the joint operator document known as the Multi Carrier Forum (MCF).
For example a 'Passive DAS" globally often refers to an offair repeater based system, whereas in Australia that is not the case.