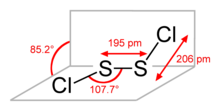
Disulfur dichloride
Disulfur dichloride is a yellow liquid that fumes in moist air due to reaction with water: It is produced by partial chlorination of elemental sulfur.
When treated with hydrogen sulfide, polysulfanes are formed as indicated in the following idealized formula: It reacts with ammonia to give tetrasulfur tetranitride as well as heptasulfur imide (S7NH) and related S−N rings S8−n(NH)n (n = 2, 3).
In the presence of aluminium chloride (AlCl3), S2Cl2 reacts with benzene to give diphenyl sulfide: Anilines (1) react with S2Cl2 in the presence of NaOH to give 1,2,3-benzodithiazolium chloride (2) (Herz reaction) which can be transformed into ortho-aminothiophenolates (3), these species are precursors to thioindigo dyes.
It is also used in cold vulcanization of rubbers, as a polymerization catalyst for vegetable oils and for hardening soft woods.
[11] S2Cl2 can be used to produce bis(2-chloroethyl)sulfide S(CH2CH2Cl)2, known as the mustard gas:[11] Consequently, it is listed in Schedule 3 of the Chemical Weapons Convention.