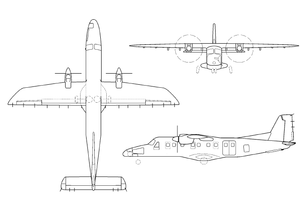
Dornier 228
In 1983, Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) bought a production licence and manufactured another 125 aircraft in Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh, India.
The fuselage, wings and tail unit are manufactured by HAL in Kanpur, India, and transported to Oberpfaffenhofen, where RUAG Aviation carries out aircraft final assembly.
[5] In the late 1970s, Dornier GmbH developed a new kind of wing, the TNT (Tragflügel neuer Technologie – Aerofoil new technology), subsidized by the German Government.
[9] In November 1983, a major license-production and phased technology-transfer agreement between Dornier and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) was signed; a separate production line was established and produced its first aircraft in 1985.
[16] The final assembly for the type is located in Germany; however, most airframe subassemblies, such as the wings, tail and fuselage, are produced by HAL in India.
[1][17][18] The main changes from the previous Dornier 228-212 model were a new five-blade propeller made of composite material, more powerful engines and an advanced glass cockpit featuring electronic instrument displays and other avionics improvements.
[24] On 30 September 2020, US firm General Atomics bought the Dornier 228 production line in Oberpfaffenhofen, including the transfer of all 450 employees, pending regulatory approval.
The aircraft was so far being manufactured under licence from RUAG for Indian defence forces and European markets would now be allowed to operate in India for commercial purposes.
[28] Alliance Air signed an agreement with Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) to lease two 17-seater Dornier 228 aircraft in September 2021.
Partners include MTU Aero Engines and Siemens, of which Rolls-Royce plc is acquiring the electric propulsion unit.
[31] On 19 January 2023, ZeroAvia flew its Dornier 228 testbed for 10 minutes with one TPE331 turboprop replaced by a prototype hydrogen-electric powertrain in the cabin: two fuel cells and a lithium-ion battery for peak power, towards a certifiable configuration by 2025.
The Dornier 228 is commonly classified as a Short Takeoff and Landing (STOL)-capable aircraft, being capable of operating from rough runways and in hot climates.
RUAG Aviation have claimed that no other aircraft in the same class may carry as much cargo or as many passengers over a comparable distance as fast as the Dornier 228 NG.
[6][34] Benefits of this wing over conventional methodology include a 15% reduction in weight, the elimination of 12,000 rivets, and lowering the per-aircraft manufacturing workload by roughly 340 man hours.
Special missions include maritime surveillance, border patrol, medevac, search and rescue, paradrop and environmental research missions, in which capacity the type has proven useful due to a ten-hour flight endurance, a wide operating range, low operational cost, and varied equipment range.
Amongst the principal changes is the adoption of Universal's UNS-1 glass cockpit, which means that standard aircraft are equipped to be flown under single-pilot instrument flight rules (IFR) in addition to visual flight rules (VFR); according to RUAG Aviation, the Dornier 228 NG is the first aircraft in its class to be certified with equivalent electronics.
[9] Additional changes include the Garrett TPE331-10 engines, which have been optimized to work with the redesigned five-bladed fibre-composite propellers now used by the type, which are more efficient, quick to start, and produces substantially less vibration and noise than the original metal four-bladed predecessor.