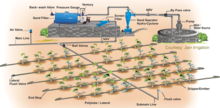
Drip irrigation
Drip irrigation systems distribute water through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters.
Fan Shengzhi shu, written in China during the first century BCE, describes the use of buried, unglazed clay pots filled with water, sometimes referred to as Ollas, as a means of irrigation.
[5] The usage of plastic to hold and distribute water in drip irrigation was later developed in Australia by Hannis Thill.
[5] Usage of a plastic emitter in drip irrigation was developed in Israel by Simcha Blass and his son Yeshayahu.
The first experimental system of this type was established in 1959 by Blass, who partnered later (1964) with Kibbutz Hatzerim to create an irrigation company called Netafim.
[1] The introduction of this technology was revolutionary according to the Times of Israel and could save 70% of water usage in the growth of rice.
[7] Goldberg and Shmueli (1970)[8] developed a significant improvement: "in the Arava desert in southern Israel [Shmueli] demonstrated that a trickle-irrigation system installed on the soil surface worked exceptionally well in producing vegetable crops, even with saline water (Elfving, 1989).
Their improvement prevailed: "Drip irrigation is presently the most efficient means to apply water to crops (Pathak et al. 2009; Goyal 2012)...
In the TOI article it was reported that N-Drip system led to yield increases of up to 33%, fertilizer reduction of 50%, a drop in greenhouse gases like carbon and methane from 50% to 85% as well as water savings of 50%.
Careful study of all the relevant factors like land topography, soil, water, crop and agro-climatic conditions are needed to determine the most suitable drip irrigation system and components to be used in a specific installation.
As of 2012, China and India were the fastest expanding countries in the field of drip- or other micro-irrigation, while worldwide well over ten million hectares used these technologies.
[17] That year, Israel's Netafim was the global market leader (a position it maintained in 2018[18]), with India's Jain Irrigation being the second-biggest micro-irrigation company.
Virtually all drip irrigation equipment manufacturers recommend that filters be employed and generally will not honor warranties unless this is done.
Fertilizer savings of up to 95% are being reported from recent university field tests using drip fertigation and slow water delivery as compared to timed-release and irrigation by micro spray heads.
In very arid regions or on sandy soils, the preferred method is to apply the irrigation water as slowly as possible.
Pulsed irrigation is sometimes used to decrease the amount of water delivered to the plant at any one time, thus reducing runoff or deep percolation.
Drip irrigation kits for home gardens are increasingly popular for homeowners and consist of a timer, hose, and emitter.