Electric field
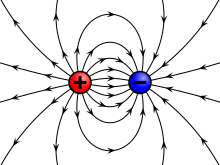
Similarly, an electric field is stronger nearer charged objects and weaker further away.
Similarly, the interaction in the electric field between atoms is the force responsible for chemical bonding that result in molecules.
[2][3][4] The SI unit for the electric field is the volt per meter (V/m), which is equal to the newton per coulomb (N/C).
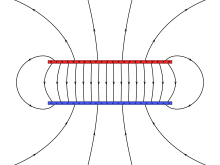
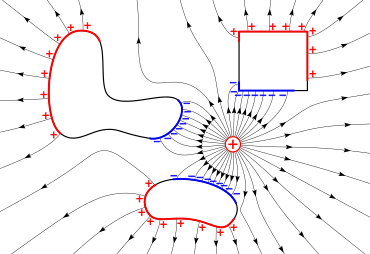
More or fewer lines may be drawn depending on the precision to which it is desired to represent the field.
[8] The study of electric fields created by stationary charges is called electrostatics.
The study of magnetic and electric fields that change over time is called electrodynamics.
In the special case of a steady state (stationary charges and currents), the Maxwell-Faraday inductive effect disappears.
have the same sign this force is positive, directed away from the other charge, indicating the particles repel each other.
When the charges have unlike signs the force is negative, indicating the particles attract.
where The superposition principle allows for the calculation of the electric field due to a distribution of charge density
which justifies, a posteriori, the previous form for E. The equations of electromagnetism are best described in a continuous description.
Such fields are present when systems of charged matter are stationary, or when electric currents are unchanging.
[18] Electrostatic and gravitational forces both are central, conservative and obey an inverse-square law.
As E and B fields are coupled, it would be misleading to split this expression into "electric" and "magnetic" contributions.
Accordingly, decomposing the electromagnetic field into an electric and magnetic component is frame-specific, and similarly for the associated energy.
Since E and P are defined separately, this equation can be used to define D. The physical interpretation of D is not as clear as E (effectively the field applied to the material) or P (induced field due to the dipoles in the material), but still serves as a convenient mathematical simplification, since Maxwell's equations can be simplified in terms of free charges and currents.
[21][20] For linear, homogeneous, isotropic materials E and D are proportional and constant throughout the region, there is no position dependence:
The invariance of the form of Maxwell's equations under Lorentz transformation can be used to derive the electric field of a uniformly moving point charge.
The charge of a particle is considered frame invariant, as supported by experimental evidence.
The above equation reduces to that given by Coulomb's law for non-relativistic speeds of the point charge.
[23] Special theory of relativity imposes the principle of locality, that requires cause and effect to be time-like separated events where the causal efficacy does not travel faster than the speed of light.
[26] Maxwell's laws are found to confirm to this view since the general solutions of fields are given in terms of retarded time which indicate that electromagnetic disturbances travel at the speed of light.
Advanced time, which also provides a solution for Maxwell's law are ignored as an unphysical solution.For the motion of a charged particle, considering for example the case of a moving particle with the above described electric field coming to an abrupt stop, the electric fields at points far from it do not immediately revert to that classically given for a stationary charge.
On stopping, the field around the stationary points begin to revert to the expected state and this effect propagates outwards at the speed of light while the electric field lines far away from this will continue to point radially towards an assumed moving charge.
This virtual particle will never be outside the range of propagation of the disturbance in electromagnetic field, since charged particles are restricted to have speeds slower than that of light, which makes it impossible to construct a Gaussian surface in this region that violates Gauss's law.
Another technical difficulty that supports this is that charged particles travelling faster than or equal to speed of light no longer have a unique retarded time.
Since electric field lines are continuous, an electromagnetic pulse of radiation is generated that connects at the boundary of this disturbance travelling outwards at the speed of light.
[29] There exist yet another set of solutions for Maxwell's equation of the same form but for advanced time
The above equation, although consistent with that of uniformly moving point charges as well as its non-relativistic limit, are not corrected for quantum-mechanical effects.
Electric field infinitely close to a conducting surface in electrostatic equilibrium having charge density