Earthworks (archaeology)
Shallow earthworks are often more visible as cropmarks or in aerial photographs if taken when the sun is low in the sky and shadows are more pronounced.
[19] For example, earthworks from deserted medieval villages can be used to determine the location, size, and layout of lost settlements.
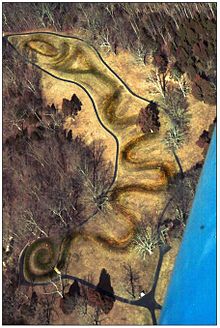
Located in Ohio, this 411-metre-long (1,348 ft) earthen work is thought to memorialize alignments of the planets and stars that were of special significance to the Native Americans that constructed it.
[23] The earthworks at Poverty Point occupy one of the largest-area sites in North America, as they cover some 920 acres (320 ha) of land in Louisiana.
[25] The largest earthwork fort built during the war was Fortress Rosecrans, which originally encompassed 255 acres (103 ha).[26][relevant?]
In northeastern Somalia, near the city of Bosaso at the end of the Baladi valley, lies an earthwork 2 to 3 km (1.2 to 1.9 mi) long.
On the south shore of the Katonga river, the Bigo earthworks consist of a series of ditches and berms comprising an outer arch that encompasses four interconnected enclosures.