Educational attainment in the United States
[4] At a national level, reports show rates of educational attainment by age, sex, race, and Hispanic origin.
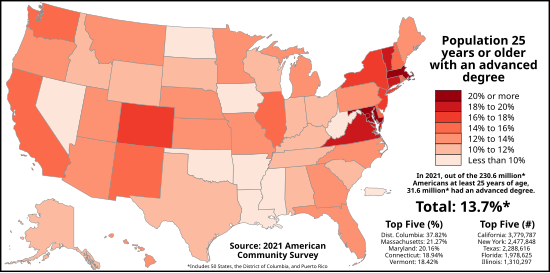
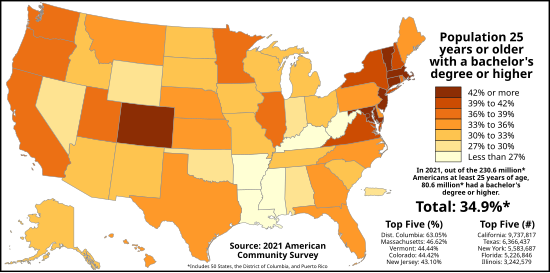
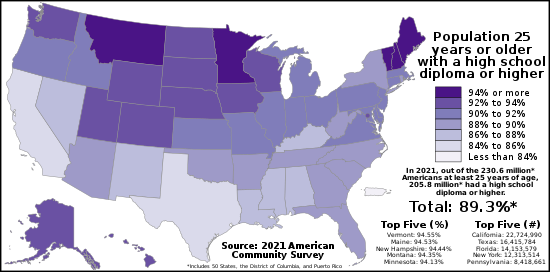
Differing at the regional and state levels, educational attainment data are shown by sex, race, and Hispanic origin (not age).
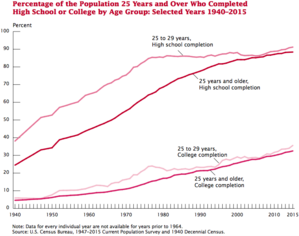
This increase follows a general trend that the Current Population Survey has shown since educational attainment was first measured in 1947.
For adults aged between 25 and 30, the percentage of either high school graduates or GED obtainers was roughly 50% in 1950 versus 90% today.
[3] According to The United States Census Bureau,[4] from 1940 to 1980, respondents were asked to what their highest grade or year of school completed was.
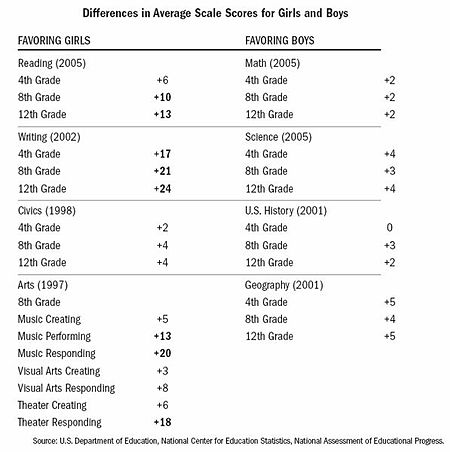
In the 1970s and 1980s, data showed girls trailing behind boys in a variety of academic performance measures, specifically in test scores in math and science.
shows the general trend of girls outperforming boys in academic achievement in terms of class grades across all subjects and college graduation rates, but boys score higher on standardized tests and are better represented in higher-paying and more prestigious STEM fields (science, technology, engineering, and math).
[8][9][10] A recent study has since discovered that many schools are not heavily focused in the performance of how young males grow in their educational development as they are with girls.
New studies have shown that, when it comes to completing their education, women are pushed to go after a bachelor degree but that financial issues affect them.
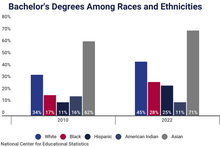
[22] The Racial achievement gap in the United States refers to these educational disparities between differing ethnic groups.
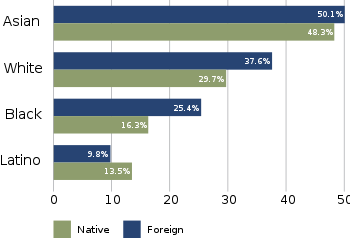
[3] Even though African immigrants are claimed to have higher educational attainment rates than any other group, they were the hardest hit during the recession beginning in 2007.
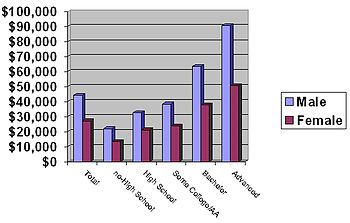
[31] SOURCE: US Census Bureau, 2018[33][34] The change in median personal and household income since 1991 also varied greatly with educational attainment.
[3] However, Asian Americans as a whole earn more than any other race due to a greater percentage of them being educated overall, an example of Simpson's paradox.
The rising demand for skilled workers indicates that job markets are able to accommodate an increasing number of highly qualified individuals, offering them improved employment opportunities.
[37] In the foreseeable future, their unemployment risk is expected to escalate further due to the likelihood of automation affecting many jobs that require lower qualifications.
[41] Using data from the 1987–88 National Survey of Families and Households,[42] Evelyn L. Lehrer found that the religion with the highest level of educational attainment was Jews, that Catholics and mainline protestants fell in the middle, and fundamentalists had the lowest levels of educational attainment.
[43] Michael A Kortt and Joseph Drew found that educational attainment in regards to religion can change with time.
Specifically they found that: Educational attainment among the population aged 25 and above varied rather slightly with geography region.
The South which had by far the largest population with roughly sixty-six million people had the lowest educational attainment at every level.
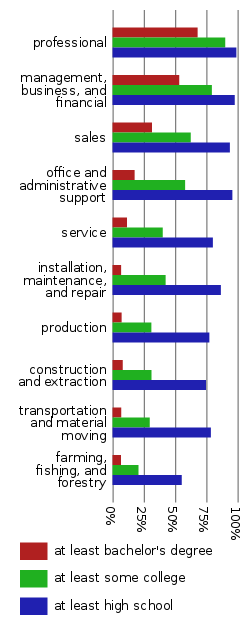
Not only is a high educational attainment a status symbol by itself, but it is also very closely related to the other two main indicators of social class: occupation and income.
A graduate degree and the roughly seven to eight years of post-secondary education serve as the main requirement for entering the "professions" and becoming part of the professional middle class.
[45][47] Overall, educational attainment is the main entrance barrier into more privileged parts of the middle class as it is not only of high value but is also the requirement for becoming a professional and earning the corresponding income.
Education is not only the main requirement for becoming a member of the professional middle class, it is also key to a comfortable lifestyle and economic security.
Increasingly however even the professional middle class is facing lay-offs and job elimination due to downsizing and replacement of full-time workers with part-time workers—this is particularly evident in colleges and universities where, by 2009, half of the faculty were part-time; another 25% were full-time but with short-term contracts, thus showing that advanced education is not necessarily associated with high salaries and economic stability.
In 1977, Pierre Bourdieu presented the idea that education leads to social reproduction and a stratified society by honoring the cultural capital of elite classes.
By rewarding the desired cultural capital with high academic achievement, upper classes are able and prepared to reach higher levels of educational attainment.
Laureau further explains that schools firmly encourage and expect parents to use concerted cultivation as a child-rearing strategy.
Randall Collins contributed the idea of credentialism to the study of class-based differences in educational attainment.
Collins maintains that public schools are socializing institutions that teach and reward middle-class values of competition and achievement.
In this view, elites are selectively separated from other students and placed into prestigious schools and colleges, where they are trained to hold positions of power.